|
|||
|
Humanoid Robot Sensors
|
|||
|
What Sensors Do Humanoid Robots Have?
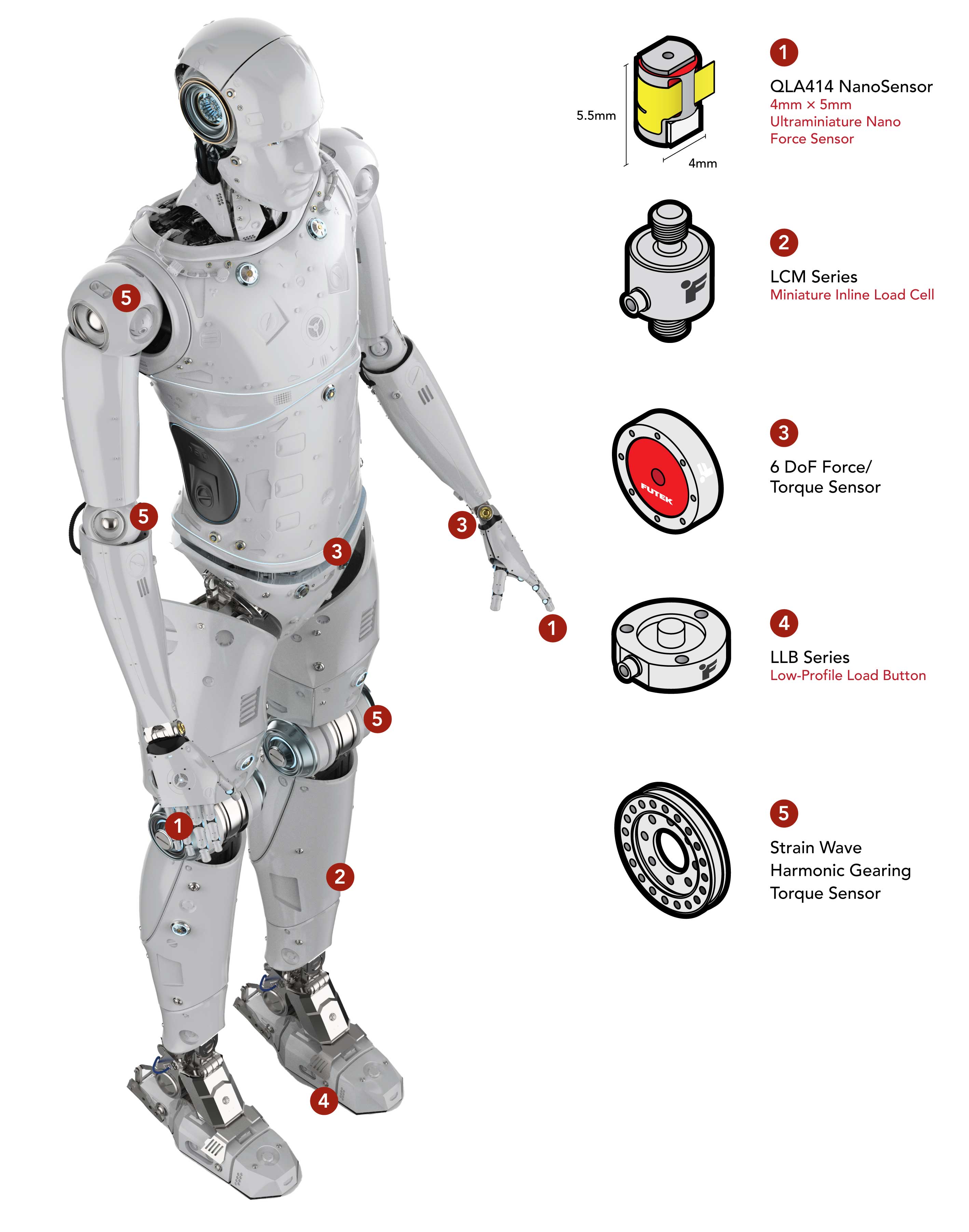
Humanoid robots are advancing rapidly to assist and support human activities, paving the way for significant technological advances that open a wide range of applications across a wide range of sectors ranging from providing assistance to clinical tasks, and support to patients, up to automating repetitive and potentially dangerous tasks for various applications that increase the efficiency of industrial operations. Central to this progress is the integration of force and torque sensors that utilize strain gauge technology that allows robots to move with a human-like grace with precision and accuracy. Collaboration among engineers, designers, and sensor manufacturers is essential to overcome challenges including managing integration complexity, adapting to environmental variability, dynamic responsiveness, cost-effectiveness, minimizing mechanical crosstalk, ensuring durability, and compliance with safety standards. FUTEK’s engineering team has deep expertise in designing and customizing force and torque sensors to overcome and meet the challenges of humanoid robot innovations. Explore how FUTEK’s expertise in force and torque sensors is utilized in major humanoid robotic systems.
Benefits of FUTEK 6 DoF Force/Torque Sensor:
|
|||
|
How it Works
|
|||
|
|||
|
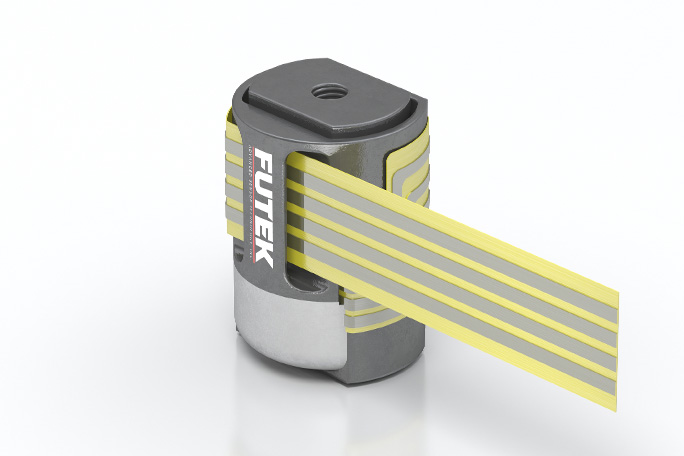
The seam-welded stainless-steel body provides outstanding strength and corrosion resistance and provides enhanced protection against physical damage in addition to withstanding other harsh environmental conditions.
Some models can be ordered with IP67 rating that can withstand submersion in one meter of water for at least 30 minutes. This feature makes the sensor “Weather rated” or “Outdoor rated" and opens up the application possibilities as it will allow outdoor usage in wet, rainy, or highly humid conditions.
Some inline force measurement applications may require an LCB200 Rod End Load Cell designed for applications involving Inline Actuators or Hydraulic Jacks with Male/Female Threads. LCB200 biggest benefit is that it features a male/female thread that can extend an actuator with fewer adapters and components needed.
3) 6 DoF F/T Sensor – Wrists, Connection joint of the torso to the lower body Sensors in the torso joints of humanoid robots make movements smooth like twisting, bending, and turning, ensuring the robot can handle its own weight and the forces it encounters during movement. Wrist systems on a humanoid robot increase dexterity and operation range for different optimized tasks required. FUTEK’s 6 DoF F/T Sensors are designed to accurately measure the forces and torques applied in one direction with little or no cross-talk interference from force or moments applied in other directions. This feature is particularly important to achieve the level of precision and dexterity required for different operation tasks executed with arm-torso system.
The foot system of humanoid robots, equipped with integrated load cells and force sensors, not only supports the robot's weight but also senses external forces exerted on the ground. This force feedback provides critical information on foot posture and external forces, enabling precise measurement of the robot's center of gravity and enhancing its autonomy. By accurately assessing these forces, the robot can maintain balance and adapt to varying conditions, thereby maximizing its operational independence. FUTEK’s LLB Series Low Profile Miniature load button is capable of measuring compression forces with a small footprint. LLB Series features a highly customized strain element designed to allow more strain measurement around the active sensor element which reduces reproducibility errors from off-axis loads, as well as internally embedded zero balance and thermal compensation, allowing for outstanding sensor reliability, accuracy, and performance. It delivers a remarkably high natural frequency which provides a fast response time that benefits accuracy and cycle time reduction in dynamic applications such as the bottom of the foot in humanoid robots. Mounted between the robot’s shoulders, knees, and elbows and mounting points, the strain wave gearing torque sensor measures the torque output during movement on each joint. The benefits in humanoids applications are:
|
|||
|
Products in Use
|
|||





LCM300-MINIATURE-THREADED-IN-LINE-LOAD-CELL-1_THUMB.jpg)
LCB200-IN-LINE-ROD-END-LOAD-CELL-1_THUMB.jpg)

LLB250-MINIATURE-LOAD-BUTTON-1_THUMB.jpg)