
Monitoring the clamping position of tools
Often, initiators and switching rings, which provide a switching signal, are used to monitor the clamping position in high-performance tool machines. However, these require complex adjustment and set up. Analog sensors from the Micro-Epsilon LVP series offer significant improvements. The cylindrical sensor is integrated into the release device and directly measures the clamping stroke of the drawbar. On the drawbar, a ring is fastened, which acts as the target for the sensor. The LVP sensor can be universally used with the most varied types of tool due to an extremely compact sensor design. The sensor supplies an analog signal according to the stroke motion of the drawbar when clamping the tool. Consequently, continuous monitoring is possible without the switching point having to be laboriously set mechanically. The miniaturized sensor electronic unit can either be accommodated at the point of measurement or in the control cabinet. Thanks to its high accuracy, the LVP sensor contributes significantly to meeting the ever increasing demands on machine tool precision and availability. |

Compensating for axial extension of milling spindles
Due to high machining speeds and the heat generated, the linear thermal expansion in milling spindles needs to be compensated for in order to keep the tool in a defined position at all times. The SGS sensor developed by Micro-Epsilon measures the thermal and centrifugal force expansion of the spindle. As well as measuring linear thermal expansion, the temperature of the sensor is also detected and output. |

Foreign body detection in medical technology
In this application, the MDS sensor recognizes foreign bodies in blister machines during the tablet packaging process. Via the movement of overhead touching rollers, foreign bodies between the blister packaging and covering material can be detected. Exceeding a pre-defined point triggers an alarm. |

Valve lift measurement in the food industry
During the filling of drinks cartons, the exact dosage is a critical factor. The sensor measures the valve lift of the filling line and requests several switching points in a measuring range of 35mm. The sealed stainless steel housings of the MDS-45-Mxx series are ideal for the food industry. |

Monitoring embossment depth
In embossing machines, car body IDs are punched into the vehicle frame. The embossment depth must be in a defined tolerance range. In order to position the embossing tool, laser triangulation sensors from Micro-Epsilon detect the distance between the embossing tool and the component. After the embossment is finished, the sensor measures the profile of the embossment and ensures that all characters are embossed to the required depth. |
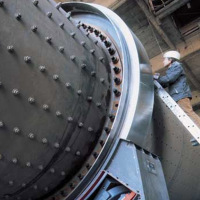
Monitoring oil gaps in hydrostatic bearings
Hydrostatic bearings are used in large plant and machinery such as stone mills, telescopic installations etc. Monitoring the gap size is a critical factor, as any disturbances in the hydraulics can cause pressure drops, which in extreme cases, can cause the gap to close, resulting in damage to the bearings and ultimately system failure. Here, it is important to have a system that is easy to install as also ageing plants have to be retrofitted. Due to the long service life and the worldwide use of this plant, the sensor should be easy to replace. For this reason, non-contact eddy current displacement sensors of the eddyNCDT 3001 series are used. |

Web-edge detection in the calender of a paper machine
If movement of the paper web in the calender is not exactly executed in one line, the heated calender roller is pressed directly onto the coating of the opposite roller, which can damage it. Repairing this special coating or even replacing the whole roller would be very costly, which is why it is mandatory to control the position of the web edge. This is where laser line sensors from Micro-Epsilon are utilized, transferring the exact position of the web edge directly to the machine control system. |

Temperature measurement for injection mould applications
Users of injection molding machines for plastics processing are facing increased quality requirements imposed by end-users, in particular for automotive applications. Because of this trend, the importance of inline temperature control right after extrusion as a global quality attribute is growing. |

Active compensation for movements in the measurement process
Harsh industrial environments place high demands on optical displacement sensors – precise measurements must still be possible despite dust and high processing speeds. The optoNCDT 1750 and optoNCDT 2300 series of laser sensors have overcome these challenges for many years. However, if motion disturbances (e.g. belt movements, radial movements of pulleys, and base body vibrations) occur that are greater than the object being measured, the measurement process may be impeded or made impossible, for example folds in a belt. |

Fluid level measurement of aluminum pig irons
In aluminum casting plants or foundries, the cast is poured into shape to form small bars, known as pig irons. The charging level in the forming process is critical in ensuring consistent weight of the pigs. Using a special non-contact measuring device, the depth of fill is recorded. For these applications, an Austrian system builder uses laser scanners. |
