 |
|
|
Plastics production and processing
|
|
Micro-Epsilon offers a wide range of sensors and solutions for non-contact measurement of plastics production. Dimensions, thickness, temperature, colors and embossing patterns in roll or sheet form can be reliably measured in a wide range of process steps from extrusion via molding to further processing. |
|
|
Two-sided thickness measurement
|
 |
Depending on the respective measurement task, it is sensible to carry out a two-sided thickness measurement. Arranged opposite the material, two displacement sensors detect the thickness. This measurement arrangement is particularly suitable for high speed measurements and fluttering materials. Micro-Epsilon also offers sensors and turnkey systems for two-sided thickness measurements.
  Measuring and inspection systems for plastics Measuring and inspection systems for plastics
|
|
|
|
Defect recognition on worktops
|
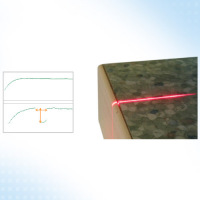 |
Foreign bodies, uneven distribution of the adhesive or unevenness when closing may produce open joints between the top material and the sidebars. The scanCONTROL laser profile sensors check if there are open joints and detect their gap size.
  Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements
|
|
|
|
Thickness profile measurement of strips and plates
|
|
|
|
|
Temperature monitoring of thin plastic films
|
 |
With blown film extrusion, non-contact temperature measurement is a difficult measurement task. Ambient radiation also penetrates thin films and distorts the intrinsic radiation of the films. The infrared CT-P3 and CT-P7 pyrometers only detect the infrared radiation emitted by the plastic films and ignore the penetrated ambient radiation. This is how high precision detection of the surface temperature is possible.
  Infrared pyrometers for universal measurements Infrared pyrometers for universal measurements
|
|
|
|
One-sided thickness measurement of films
|
 |
In its sensor housing, the combiSENSOR combines an eddy current displacement sensor and a capacitive displacement sensor. This unique sensor concept enables one-sided thickness measurement of electrically non-conductive materials on metallic objects. Its field of application is the thickness measurement of plastic film or of plastic coating on metal plates. Connected to the sensor via a cable, the controller processes and calculates the signals in order to put them out via interfaces.
  One-sided thickness measurement of plastics One-sided thickness measurement of plastics
|
|
|
|
Thermography for injection molding processes
|
 |
moldCONTROL is a thermography solution for recognizing quality fluctuations in injection molding production. The compact, industrial thermal imaging camera captures a thermal image of the component directly after the injection molding process. The software compares the infrared images associated with the component (actual) to stored references (target). The identified temperature differences provide the basis for a good/bad decision reported back to the handling system.
|
|
|
|
Gap measurement of extruded plastic profiles
|
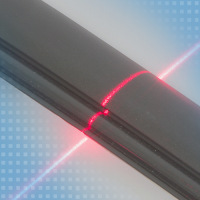 |
In the extrusion of high quality plastic profiles, adherence to tight manufacturing tolerances is crucial. For quality assurance, laser profile scanners from Micro-Epsilon are used. Thanks to the surface compensation, the scanners reliably detect the profiles of black rubber surfaces. For gap measurement, special software packages are available with which different parameters can be easily selected.
  Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements
|
|
|
|
Surface defect detection of plastic attachments
|
 |
Surfaces play an important role in the functionality and aesthetics of plastic components. Therefore, optical surface inspection is a central approach for 100% quality control. Deflectometer-based inspection systems from Micro-Epsilon inspect shiny surfaces and detect even the smallest of deviations. The defects found are evaluated and displayed in the 3D model.
  Sensors for painting and paint inspection Sensors for painting and paint inspection
|
|
|
|
Inline color measurement of transparent films
|
 |
As well as color fluctuations, streaks can occur during production. With translucent films, the film color is measured very accurately and quickly using the ACS7000 color measuring system together with the ACS3 transmission sensor.
  High Speed Photospectrometer colorCONTROL ACS7000 High Speed Photospectrometer colorCONTROL ACS7000
|
|
|
|
Color measurement of extruded parts
|
 |
In order to avoid defective production and to conserve resources during the extrusion of plastic products, it is crucial to recognize color deviations not just at the end of the process chain but already during the ongoing process. The accurate colorSENSOR CFO color sensors are used for color recognition in the process and transmit color deviations directly to the control system.
  Compact True Color Sensor Compact True Color Sensor
|
|
|
|
Inline color measurement of plastic injection-moulded parts
|
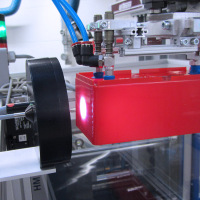 |
In plastic injection moulding, the exact color shade of the products is important, as the color changes during cooling. To date, it has only been possible to measure random samples of cooled pieces. However, the colorCONTROL ACS inline color measurement system from Micro-Epsilon can 100% inspect the products as they are extracted from the mould.
  High Speed Photospectrometer colorCONTROL ACS7000 High Speed Photospectrometer colorCONTROL ACS7000
|
|
|
|
Surface inspection of adhesive film
|
 |
In industry, the need for adhesive film is increasing. When producing the film, depressions and folds often occur, rendering the film unusable. Therefore, the customers’ requirements for an impeccable surface are increasing. For this purpose, a scanCONTROL 2910-100 laser scanner can be used.
  Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements
|
|
|
|
Temperature measurement for injection mould applications
|
 |
Users of injection molding machines for plastics processing are facing increased quality requirements imposed by end-users, in particular for automotive applications. Because of this trend, the importance of inline temperature control right after extrusion as a global quality attribute is growing.
  Thermal imaging cameras for industrial temperature monitoring Thermal imaging cameras for industrial temperature monitoring
|
|
|
|
Non-contact film thickness measurement
|
 |
In film production inline thickness measurement guarantees constant product quality. Micro-Epsilon's KS5 combination sensor measures the thickness of films in a non-contact and thus wear free process.
  One-sided thickness measurement of plastics One-sided thickness measurement of plastics
|
|
|
|
Thickness measurement using displacement sensors
|
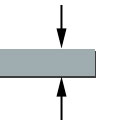 |
Thickness measurement using displacement sensors is a wide application area. Basically there are distinctions between non-destructive/destructive, non-contact/with contact and one-side/two-sided thickness measurement. The Micro-Epsilon measuring techniques for thickness measurement are all emission-free whereby no emissions regulations of any kind have to be complied with. Thickness measurements must be performed both with contacting as well as with non-contact sensors whereby non-contact measuring techniques show advantages as regards accuracy and measuring speed. There is also a distinction between one-sided and two-sided thickness measurement. Two-sided thickness measurements are carried out with at least one pair of sensors which are installed together on one axis. This pair of sensors measures the target synchronously. The difference between the measurement results (C-A-B) produces the thickness of the measuring object. One-sided thickness measurements must only be performed with non-contact sensors. In doing so, the target is only measured with one sensor and either only a part of the target thickness (e.g. layer thickness) or the complete measuring object thickness is measured. Thickness measurements are mainly used in process control and quality assurance, e.g. for the control of extrusion systems or 100% checking of tube diameters.
  Capacitive displacement sensors and measurement systems Capacitive displacement sensors and measurement systems
  Inductive sensors (eddy current) for displacement, distance & position Inductive sensors (eddy current) for displacement, distance & position
  optoNCDT Laser Sensoren optoNCDT Laser Sensoren
  Inspection systems for inline quality control Inspection systems for inline quality control
|
|
|
|
Blown film thickness
|
 |
The thickness of blown films is an important aspect in terms of constant quality in blown film production. During production, strong thickness tolerances can occur. The blown film system from Micro-Epsilon measures the profile of the film with or without contact directly after the extrusion nozzle. Located on a reversing frame, the system continuously traverses the film tube and provides the data to the host system for controlling the extrusion nozzle.
  Thickness profile measurement of blown films (non-contact and contact measurement 10µm to 500µm) Thickness profile measurement of blown films (non-contact and contact measurement 10µm to 500µm)
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
Paint inspection
|
|
The monitoring of painted objects is becoming increasingly important in the context of high quality requirements. Defect detection directly after the painting process as well as color measurement and color comparison at the incoming goods inspection are frequent measuring tasks, where high precision and repeatability are required. |
|
|
Fully automatic paint defect inspection of car bodies and attachments
|
 |
Particularly with shiny surfaces, a faultless production chain is expected in order to lend a sophisticated visual appearance to the final product. For fully automatic defect detection on car bodies and attachments, the reflectCONTROL inspection system is used. The system projects a striped pattern onto the surface. Deviations caused by defect are recorded with two cameras and evaluated via software.
  Fully automatic surface inspection of painted car bodies Fully automatic surface inspection of painted car bodies
|
|
|
|
Color recognition of kitchen fronts
|
 |
In order to ensure consistent color of different front panels, color sensors from Micro-Epsilon are used. The sensors inspect the color of the kitchen fronts in the painting plant. Color sensors ensure that the color shade is within the specified tolerances. Even the smallest color deviations imperceptible to the human eye can be detected reliably.
  Compact True Color Sensor Compact True Color Sensor
|
|
|
|
Color inspection and sorting of supplier parts
|
 |
Before installing front aprons, Micro-Epsilon color sensors check if the color of the attachment matches the body color. Different color groups can be defined to cover all coatings.
  Compact True Color Sensor Compact True Color Sensor
|
|
|
|
Color measurement of liquid paint
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
Mobile machines & lifting technology
|
|
In lifting technology as well as in mobile machines, the monitoring of the movement or position is required for functional and safety aspects. Micro-Epsilon sensors are used in numerous measurement tasks to ensure a controlled sequence of movement. |
|
|
Reduced risk of tipping with loading wagons
|
 |
In order to increase the safety of loading wagons, automatic braking systems are used. The brakes are activated if the lateral acceleration of a loading wagon becomes too high due to high speeds and tight curves and if the wagon threatens to tip over. The braking reduces the wagon’s speed and therefore both the lateral acceleration and the risk of tipping over. For electronic braking systems, acceleration sensors from the ACC53 series from Micro-Epsilon are used, which reliably detect the accelerations of the loading wagon.
|
|
|
|
Gap analysis in axial piston pumps
|
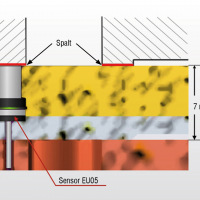 |
So far, gap measurements inside the pumps were not possible because of the extreme requirements. The sensors must be resistant to high speeds, high pressures up to 1,000 bar and temperatures above 100 °C. Furthermore, the pumps are extremely compact, which significantly limits the space available for integration of sensors. Thanks to the extremely small sensor designs and their high pressure and temperature stability, the eddyNCDT inductive miniature sensors are ideal for this application. The eddyNCDT 3300 eddy current measuring system, which is one of the most powerful systems in the world, is therefore used on the test rig for evaluating the pumps.
  eddyNCDT 3300 eddyNCDT 3300
|
|
|
|
Monitoring free-standing structures
|
 |
High, free-standing structures such as cranes are monitored using inclination sensors which provide early warnings of a possible tip over in order to avoid accidents.
|
|
|
|
Wear measurement in the bearing
|
 |
In modern marine diesel engines, the crankshaft bearing is subject to regular maintenance intervals. For predictive maintenance, inductive sensors (eddy current sensors) are used to permanently monitor the bearing wear. Despite harsh ambient conditions such as high temperatures, lubricants and pressures, the sensors measure the bearing movement reliably in long-term use.
  Inductive sensors (eddy current) for displacement, distance & position Inductive sensors (eddy current) for displacement, distance & position
|
|
|
|
Piston position in the hydraulic cylinder
|
 |
In modern hydraulic cylinders, the piston position is detected continuously. Therefore, inductive long-stroke sensors from Micro-Epsilon are used which are directly integrated in the hydraulic cylinder. Its robust design enables the sensor to provide stable measurement values despite pressure and oil.
  induSENSOR EDS induSENSOR EDS
|
|
|
|
Position detection of the piston in the hydraulic cylinder
|
 |
In order to detect the piston position of hydraulic cylinders, magnetostrictive and inductive sensors are directly integrated in the sensor. Therefore, the magneto-inductive sensor mainSENSOR is an alternative. The face-mounted magnet transfers its magnetic field to the piston rod. The sensor mounted outside then detects the magnetic field distribution along the rod and converts this into a linear output signal, which corresponds to the piston position.
  Magneto-inductive distance sensors Magneto-inductive distance sensors
|
|
|
|
Collision detection in mowers
|
 |
In agricultural machines, acceleration sensors monitor the mower in order to recognize collisions. When colliding with a stone, the mower will experience a movement that is detected by the acceleration sensors. When the mower is immediately switched off, damages can be reduced or avoided.
|
|
|
|
Jib lengths of mobile cranes
|
 |
The current jib length is important when calculating the torque of the load on the crane. This length is measured with an integrated draw-wire sensor. This simple and telescopic measuring principle makes wire sensors predestined for the task. The sensors can also be retrofitted.
  Draw-wire displacement sensors Draw-wire displacement sensors
|
|
|
|
Precision synchronized lifting system
|
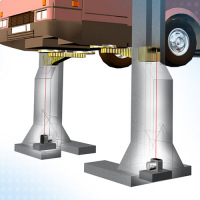 |
Synchronized lifting systems enable the raising and lowering of heavy loads controlled for distance and force or the controlled forward feed of large components. To achieve this, eight or more cylinders are connected to a central high pressure hydraulic system (700 bar). The travel displacement of each individual cylinder must be measured as the actual value for the synchronized movement and supplied to the closed/open loop controller. Draw-wire displacement sensors of the wireSENSOR Series P60 are employed for this task.
  WDS-P60 analog WDS-P60 analog
|
|
|
|
Displacement measurement on slag transporter
|
 |
Draw-wire sensors are used to reduce the standstill time of slag transporters during the loading and unloading. They are installed on the tipping cylinder and the support cylinder. In this way, the signal of a limit switch no longer has to be waited for. Depending on the load state, the transporter can start the journey earlier. The sensor also withstands this demanding environment using a special case and wire extensions.
  Draw-wire displacement sensors Draw-wire displacement sensors
|
|
|
|
Lift height of a catering vehicle
|
 |
Catering vehicles play an important role in passenger air traffic. They are responsible for there being enough foodstuffs on board. It is especially difficult with the Airbus A380 to reach the loading hatch with the vehicle. Therefore, the load area of the scissor platform is also maneuverable. Draw-wire sensors are perfectly suitable for measuring this displacement.
  Draw-wire displacement sensors Draw-wire displacement sensors
|
|
|
|
Rack control unit - lift height
|
 |
The frequently used automatic rack control units make modern warehousing much easier. These units must automatically travel long distances and position the products with millimetre precision at the end. Modern optical laser sensors and also draw-wire sensors are used to monitor this movement. Draw-wire sensors are the more economical solution for distances up to 50 metres. Laser sensors which determine the distance using time of flight measurement are suitable for larger distances. Distances can be precisely measured and loads can be exactly positioned or delivered with their help.
  Laser distance sensors for extra long ranges Laser distance sensors for extra long ranges
  Draw-wire displacement sensors Draw-wire displacement sensors
|
|
|
|
Crane support distance
|
 |
A truck-mounted crane is frequently the better solution in many cases where loads have to be lifted. As a mobile solution, safety also plays an important role here. Therefore a load torque limiter controls whether the crane can still lift or not. In order to ensure the maximum permitted load, the side crane supports must always be completely extended. If this would not be possible due to lack of space, the crane could not be put into operation. The dynamic process for measuring how far the crane supports have been extended facilitates a calculation of the permitted load capacity. Thus, the use of truck-mounted cranes can also be ensured where space is restricted..
  Draw-wire displacement sensors Draw-wire displacement sensors
|
|
|
|
Lift platform – lift height
|
 |
Side supports against tipping over are installed for lift trucks and lift work platforms. The crane or the platform can only be put into operation when the supports are completely extended so that there is also no danger of tipping in the case of long extension frames. However, sometimes this is not possible for spatial reasons. Therefore draw-wire sensors from Micro-Epsilon are used for measuring how far the supports are extended. A dynamic load torque limit across the actual support area is thus produced. Redundant measurement is performed as this is a safety relevant measured value.
  Draw-wire displacement sensors Draw-wire displacement sensors
|
|
|
|
Synchronized lifting system lift height
|
 |
Mobile lifting jacks are being used more and more often for commercial and railed vehicles. The lifting jacks for commercial vehicles are often designed as column lifts. In contrast, railed vehicles are often lifted on the frame. Any number of these lifting jacks can be combined into one system. As each lifting jack has its own drive for the lifting movement, the individual devices must be synchronized in order to ensure a completely level and oscillation-free movement. The lifting movement of each lifting jack is measured with a draw-wire sensor for this.
  Draw-wire displacement sensors Draw-wire displacement sensors
|
|
|
|
Forklift lifting height
|
 |
A large part of internal transportation is performed by forklifts. The risk of tipping the forklift when products are lifted is high. Therefore, the permitted speed has been restricted with limit switches. Draw-wire sensors from Micro-Epsilon measure the current lift height and make continuous speed regulation possible, depending on the height of the products.
  Draw-wire displacement sensors Draw-wire displacement sensors
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
Metrology and testing technology
|
|
In measuring and testing machines, the measurement technology used is the central element. Therefore, metrological parameters such as resolution and linearity are decisive factors in order to enable precise data collection. For operation in measuring and testing machines, Micro-Epsilon offers numerous measuring techniques based on highest accuracy. |
|
|
Coordinate measuring machine
|
 |
In order to measure a wide variety of components, coordinate measuring machines are used. Different gauges and measuring devices provide a 3D image of the surface component. scanCONTROL laser line scanners are ideally suitable for this purpose. Based on the triangulation principle, they measure the actual component surface without contact to micrometer accuracy.
  Confocal chromatic sensors for displacement, distance, position, thickness Confocal chromatic sensors for displacement, distance, position, thickness
|
|
|
|
Calibrating robot axes
|
 |
Industrial robots have become indispensable in modern production facilities due to their reliability and high speed. During set up and also at regular intervals within the scope of quality assurance, the robot axes must be adjusted. Here, electronic adjustment probes have already replaced mechanical probes. The measurement probes mounted on the robot axes acquire the zero point during the axis rotation using a probe tip. The integral electronics evaluates the probe signal and transmits a switching signal to the robot controller.
  induSENSOR LVDT gages DTA series induSENSOR LVDT gages DTA series
  Inductive sensors (LVDT) and gauges Inductive sensors (LVDT) and gauges
|
|
|
|
Coordinate measuring machine
|
 |
Coordinate measurement machines from Zeiss have been known for decades for the highest quality, precision and reliability. Also the mobile measurement machine, ScanMax fulfills these criteria, in part due to the application of inductive displacement sensors from Micro-Epsilon.
  Inductive sensors (LVDT) and gauges Inductive sensors (LVDT) and gauges
|
|
|
|
3D inspection and surface assessment of roof tiles
|
 |
The production of roof tiles places high demands on measurement and testing methods for ensuring constant high product quality. In the DASTOKON semi-automatic measurement and test system and in the BSPK pilot plant a laser triangulation sensor of the Series ILD 1800 is used for the 3D inspection and for surface assessment.
  optoNCDT Laser Sensoren optoNCDT Laser Sensoren
|
|
|
|
Coordinate measuring machine
|
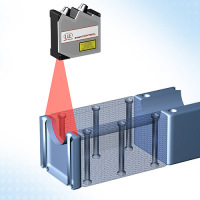 |
Coordinate measurement machines are used for measuring many different components. Different scanners and measuring equipment measure the surface of the component in three dimensions. Laser line scanners are ideally suited for this purpose. They measure the actual surface of the component without contact and with micrometre precision according to the triangulation principle.
  Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
Metal production and processing
|
|
Intelligent sensors are required in production, processing, conveyance and storage of metallic materials. There, sensors enable efficient and safe production and later failure-free processing. Micro-Epsilon has expertise and know-how in a wide range of applications: in the positioning of cranes, machine parts and materials, in the monitoring of the thickness of metal strips and slabs to the profile measurement of pressed moldings. |
|
|
Optimizing weld seams with profile measurements
|
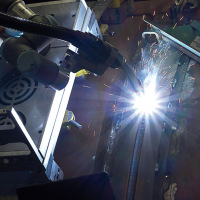 |
Inrotech A/S in Denmark relies on sensors from Micro-Epsilon to achieve optimal quality of weld seams in a fully automatic process. The company has developed a welding robot called »Inrotech-Crawler« which calculates welding processes in advance before carrying them out. Therefore, the robot uses the precise measurement values provided by the powerful laser profile scanner from Micro-Epsilon. A scanCONTROL 2900 scanner is fixed on the Inrotech-Crawler and detects the geometry of the seam to be welded before the actual welding process starts. Only these high precision profile measurements enable the process to be automated. Due to its compact, lightweight design with integrated controller, the laser profile scanner is ideally suited to this measurement task. Various connection possibilities offered by the SDK (Software Development Kit) enable the customer to directly transmit the profile data calibrated to their own software via scanCONTROL DLL. The Weldlogic technology from Inrotech then calculates, among other things, the number of welding passes, the position of the weld seams, the weld speed and the oscillation width. Directly after the calculation, the Crawler automatically performs the welding process.
  Compact laser scanner for high precision Compact laser scanner for high precision
|
|
|
|
3D measurement of components prior to plasma cutting
|
 |
In order to process these huge domes quickly, fully automatically and at extreme precision, it is necessary to determine their shape and exact position within the production line. As the pure CAD data of the dome often differs by several centimeters from the actual dimensions, the 3D profile of the covers is measured before processing using scanCONTROL 2900 laser scanners. The exact dimensions are then determined from the 2D data generated by the scanner which is connected to a 6D scanner position system. The scanning process is performed at high speeds up to 60 m/min. Therefore, a reliable hardware trigger is required to obtain the real shape of the target. Its compact design, integrated electronics and speed make the MicroEpsilon laser scanner suitable for inline integration. In addition, high performance scanners achieve a high repeatability of 50 µm/m even with different reflective properties of the metallic test objects.
  Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements
|
|
|
|
Bending/smoothness of aluminum cast covers
|
 |
After AL covers have been cast and prior to milling of the sealing surface the covers must be manually straightened and sorted into OK/NOK. This operation takes place in a rough environment (casting bay). The measuring technique that was used earlier (probes) are subject to a high degree of wear and had to be replaced in regular intervals. In order to minimize spare parts costs the customers have decided in favor of the non- contacting and non-wearing eddy-current measuring system. What is of special importance for the success of this measuring method is the fact that eddyNCDT eddy-current sensors, due to the possibility of 3-point-linearization, supply reliable measuring values even with complex target geometries.
  eddyNCDT 3300 eddyNCDT 3300
|
|
|
|
Monitoring mold deformations in aluminum die-casting
|
 |
Monitoring tool deformation using inductive sensors based on eddy current enables high product quality combined with improved tool life and reduced rework. Usually, three to four eddyNCDT 3005 eddy current systems are used to ensure consistent gap monitoring. A system consists of a compact and robust controller, which together with the cable and sensor form a solid unit. The integrated system design increases robustness and resistance to external factors, making the system insensitive to harsh industrial environments with high temperatures, dust, dirt or pressure, and delivers accurate results regardless of the environment. Due to the compactness of the eddyNCDT 3005 system, subsequent integration into an existing machine is possible at any time.
  Compact, inductive displacement measuring system for serial applications Compact, inductive displacement measuring system for serial applications
|
|
|
|
Monitoring metal sheet infeed during the pressing process
|
 |
The measurement of the distortion is carried out using several optoNCDT 1420 laser triangulation sensors, which are placed around the metal sheet, either in the tool or on the side of the tool. The arrangement is chosen in such a way that the laser beam measures on the edges of the sheet, which is between the top and bottom of the tool. Due to the extremely small measurement spot size, the laser is therefore able to measure extremely small gaps between the two tool parts of less than one millimeter. The measured values are transmitted via analog or digitally to the controller. They allow a conclusion to be drawn on how much material has flowed. This enables, for example, the pressing force to be controlled during the ongoing process, reducing waste, material consumption, downtime and costs. Micro-Epsilon laser triangulation sensors are rugged and can withstand high mechanical loads such as vibration and shock.
  Smart laser triangulation displacement sensor Smart laser triangulation displacement sensor
|
|
|
|
Coil diameter
|
 |
Rolled strips in the metal industry are wound on coils for transport. For the later processing when the coils are unwound, it is important to know how much material has already been unrolled. This task is simple to solve by using an optoNCDT ILR optical length sensor. It continuously measures onto the surface of the coil and thus records the diameter. The diameter of the coil reduces due to the unwinding which is measured using the increase in distance from the coil surface to the sensor. Using the coil thickness, the material length can be recalculated using specific algorithms.
  Laser distance sensors for extra long ranges Laser distance sensors for extra long ranges
|
|
|
|
Coil unwinding
|
 |
Rolled strips in the metal industry are wound on coils for transport. For the later processing when the coils are unwound, it is important to know how much material has already been unrolled. This task is simple to solve by using an optoNCDT ILR optical length sensor. It continuously measures the distance from the surface of the coil to the center. The thickness of the coil reduces due to the unwinding which is measured using the increase in distance from the coil surface to the sensor. Using the coil thickness, the material length can be recalculated using specific algorithms.
  Laser distance sensors for extra long ranges Laser distance sensors for extra long ranges
|
|
|
|
Measuring and inspecting laser welding seams
|
 |
Fully automatic welding units can be found in numerous industrial areas. Quality control in the form of a 100% inspection is indispensable in order to achieve defect-free weld seams. Laser profile sensors from Micro-Epsilon monitor the weld seam and immediately detect defects as well as the completeness of the width and height profile of the weld.
  Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements
|
|
|
|
Double sheet detection before pressing
|
 |
Before shaped sheets are fed into the press, laser-optical displacement sensors are used, which enable double sheet detection. Two sensors are mounted above and below the continuous sheets and provide a thickness value regardless of the exact position of the sheets.
  Extreme dynamic laser sensor with anti speckle feature Extreme dynamic laser sensor with anti speckle feature
|
|
|
|
Thickness measurement of metal strips
|
 |
When measuring the thickness of metal strips, optical methods based on laser triangulation have numerous advantages compared with other methods. They measure without contact and therefore without wear. Moreover, independently of the condition of the material it is possible to carry out an exact geometrical measurement in relation to the strip surface. Micro-Epsilon offers robust measuring systems as C-frames and O-frames which operate independently of the alloy.
  Measuring and inspection systems for the metal processing industry Measuring and inspection systems for the metal processing industry
|
|
|
|
Measurement of the zinc strip color in the production plant
|
 |
In the production of high-quality material strips and boards made out of titanium zinc, the surfaces receive specific treatment. Therefore, the coloring of the zinc products is already determined during the production process.
  High Speed Photospectrometer colorCONTROL ACS7000 High Speed Photospectrometer colorCONTROL ACS7000
|
|
|
|
Weld seam inspection on pipes
|
 |
A perfect weld seam is essential in a leak tight pipe. scanCONTROL laser scanners are therefore used during spiral welding to align the weld flanks. This results in a much more reliable welding process. The long base distance of 600mm and the protective housing for the sensor are also important here.
  Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements
|
|
|
|
Acquisition of the internal diameter of tubes
|
 |
An important criterion for the quality or the wear of tubes in industrial applications is the dimensional conformance of the internal diameter over the complete length. Where high demands are made on accuracy, a quick and reliable recording of the data must be ensured, because, for example, wear measurements must be carried out in the chemical industry on pipes which are already installed, i.e. with the plant shut down. Two pairs of sensors record two tracks offset by 90° in one measurement step.
  Non-contact inspection of extruder bores Non-contact inspection of extruder bores
|
|
|
|
Strip width when trimming metal strips
|
 |
As different widths are frequently required during the production of metal strips, the strips must be trimmed after the rolling process and both the cutters must be movable electrically. The distance is now measured by difference measurement using laser sensors from Micro-Epsilon so that compliance with the target dimensions no longer has to be checked manually as was the case previously. Two optoNCDT sensors are used for this.
  optoNCDT Laser Sensoren optoNCDT Laser Sensoren
|
|
|
|
Weld seam tracking for pipeline inspection
|
 |
Defective weld seams are often the reason for leaks on pipelines. Therefore, the seams are inspected on the outside after the welding with the profile scanner scanCONTROL. In doing so, the scanner is positioned in a testing device on the pipe. After the manual alignment, the scanner automatically inspects the weld seam and centers itself automatically on the pipe in doing so.
  Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements
|
|
|
|
High precision pipe measurement
|
 |
High precision pipe measurement Pipes, fittings and sleeves are inspected using random sampling for their dimensional accuracy in a special system. Sensors of the optoNCDT 1700 series rotate mounted on a plate. The laser beam is deflected by 90° by an adjustable mirror for the measurement. The system produces a detailed thickness profile of the target using the difference method.
  optoNCDT Laser Sensoren optoNCDT Laser Sensoren
|
|
|
|
Aluminum rim dimension
|
 |
Maximum quality is required for the production of aluminum rims so that the necessary smooth running is achieved in the subsequent use. In contrast to tactile methods, laser scanners from the Micro Epsilon scanCONTROL series are used for this. These sensors inspect the rims for all geometric defects in an integrated tester. Therefore, a 100% in-line quality control is achieved.
  Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements
|
|
|
|
Roller clearance
|
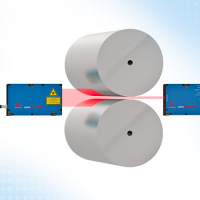 |
The distance of both rollers from each other or from the roller to the support surface is the crucial dimension for rolling processes for metals, plastics or other materials. In the case of sensitive processes and high material accuracies, the clearance must be checked constantly so that imminent rejection is avoided. The contacting inductive and the non-contact methods are suitable for this. In the case of contacting methods, the sensor is mounted on the outside on the roller guide. The change in clearance is transmitted to a plunger whose position change is measured by the inductive sensor. In the case of the non-contact method, the roller is between the transmitter and receiver of an optical micrometer. The emitted light curtain is partially covered by the roller. The remainder reaches the receiver through the gap. The gap can be calculated based on the light quantity measurement.
  High resolution optical micrometer High resolution optical micrometer
|
|
|
|
Coil edge
|
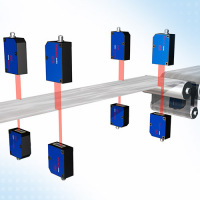 |
Rolled sheets in the metal industry are wound on coils for transport. It is important that directly before and also after the coiling, to check the position and the edge condition of the metal strip. optoCONTROL optical micrometers are used for this. If the edge of the coil is within the measuring range during the winding or unwinding, the position and the edge structure can be determined from this. This technique ensures that the coil is wound correctly and also that the correct metal strip quality has been delivered for the unwinding.
  High resolution optical micrometer High resolution optical micrometer
|
|
|
|
Tempering - temperature measurement
|
|
|
|
|
Temperature measurement of molten metal
|
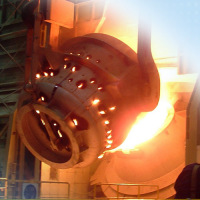 |
Temperature monitoring of liquid metal is important to maintain the corresponding process temperature during casting. With the thermoIMAGER TIM M05, Micro-Epsilon offers the right spectral range as well as a continuous measuring range of from 900 °C to 2000 °C. Due to the high frame rate of 1 kHz and the high optical resolution, thermal images can be recorded quickly and reliably.
  Infrared sensors and thermal imagers for precise temperature measurement Infrared sensors and thermal imagers for precise temperature measurement
|
|
|
|
Temperature measurement in the hot rolling mill
|
 |
In the milling line, the forming temperature between the individual rolls is measured continuously. Micro-Epsilon's non-contact infrared pyrometers measure with a short response time and from a safe distance. For the different metals and temperature ranges, IR temperature sensors and thermal cameras with different wavelengths are available.
  Infrared sensors and thermal imagers for precise temperature measurement Infrared sensors and thermal imagers for precise temperature measurement
|
|
|
|
Weld seam profile
|
 |
Welding robots which perform the joining automatically are often used for joining metals. For visible parts, the weld seam must satisfy certain optical criteria; for example, there must be no remaining welding beads. A laser scanner is installed directly after the welding head for this. It measures all the weld seams made and arranges for the robot to make corrections if necessary.
  Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements Laser scanners for 2D/3D profile measurements
|
|
|
|
Aluminum thickness
|
 |
It is important to know the thickness of the plates for the manufacture of aluminum plates. The non-contact profile measuring system measures the profile of the plates using a capacitive sensor. At the same time, the width of the plate is determined during the measurement. The reversing rolling stand and the following roller stands can be better adjusted using the data obtained. The system is integrated in the existing roller track. Installed directly before the cropping shear where the plate is stationary for the cut, the production process is not impaired.
  Inspection systems for inline quality control Inspection systems for inline quality control
|
|
|
|
|
|
|