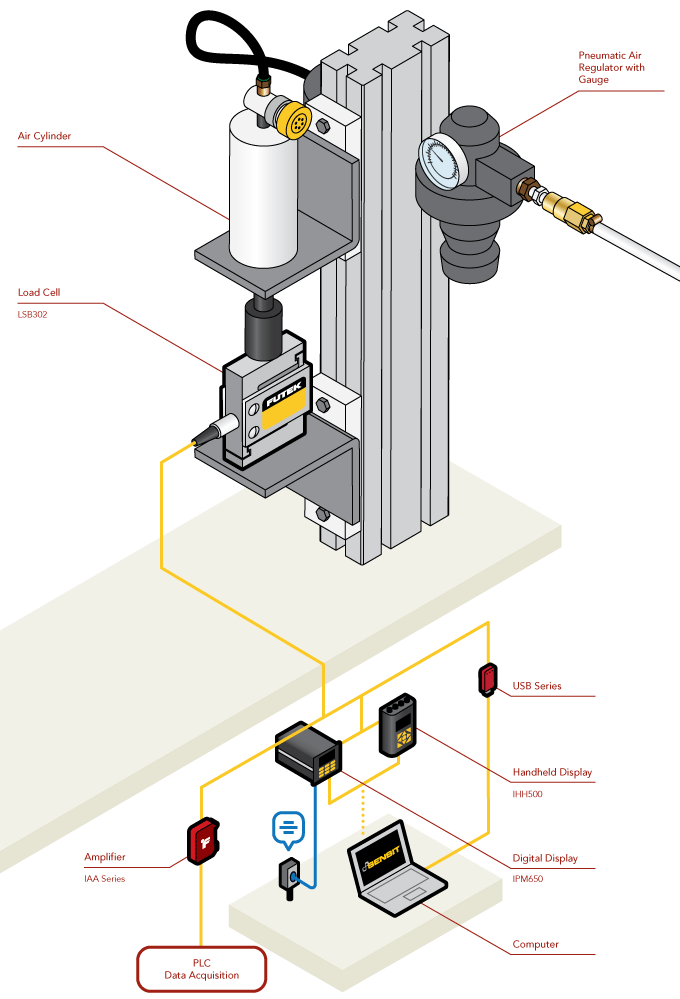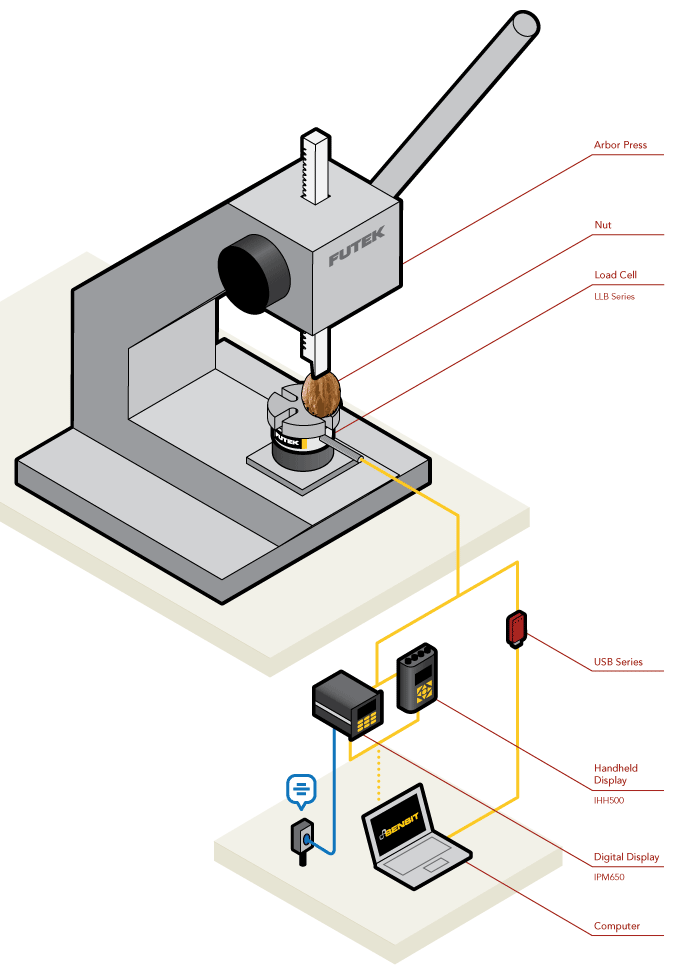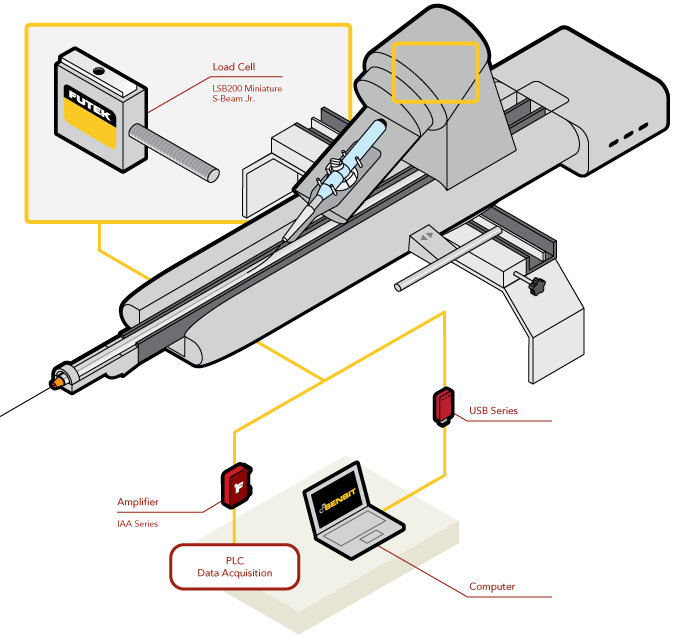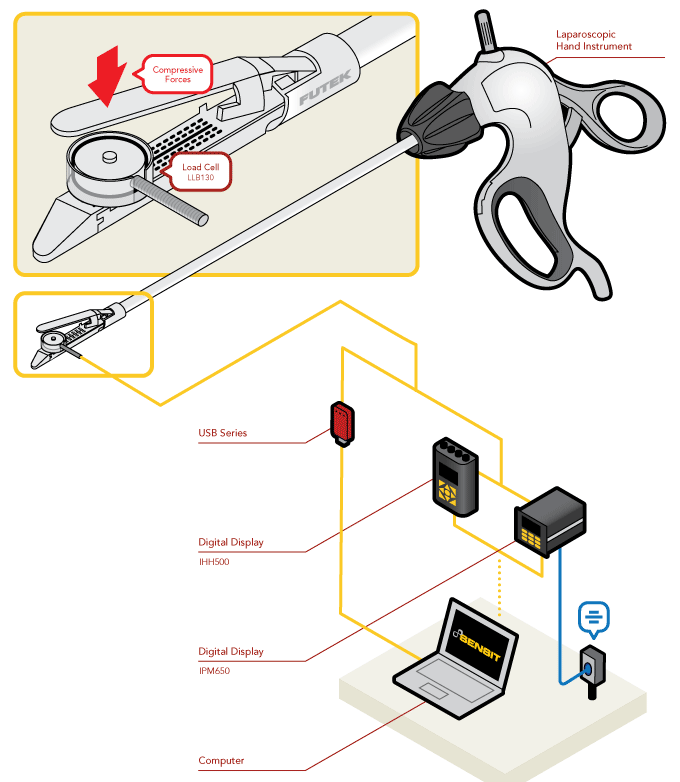
Resistance Spot Welding
How it Works
- Resistance Spot Welding is commonly used in the automotive industry for vehicle body parts.
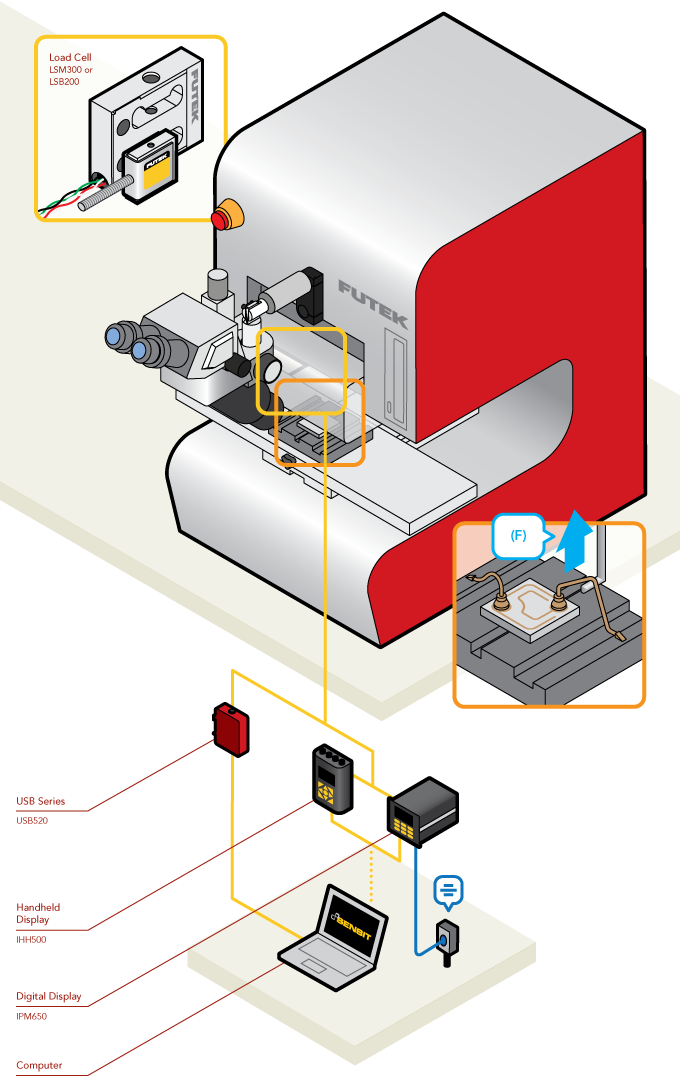
- Resistance Welding machines must apply a specific amount of pressing force with the electrodes in order to ensure that the machine will apply a proper weld.
- Load Cells can be used to measure the pressing force of a Resistance Spot Welding machine.
- In this application, FUTEK’s LLB300 Miniature Load Button is placed between the electrodes to calibrate the force applied. As force is applied by the machine, the LLB300 will sense the load measurement and can display the value on FUTEK’s IHH500 Intelligent Digital Hand Held display, FUTEK’s IPM650 Panel Mount Display, or a PC via FUTEK’s USB Solutions.
- Pairing the SENSIT™ Test and Measurement Software with any of FUTEK’s instruments provides the user with the ability to data log and live graph the measurements and store them for calibration history.
- NOTE: We recommend engineers use caution upon installation of the load cell between the electrodes, so as not to damage the LLB's housing.
|
Reliability Test Stand
How it Works
- FUTEK constructed a pneumatic test stand to extensively test the fatigue rate of our LSB302 S Beam Tension and Compression Load Cell.
- We began this test in 2001 to decipher the life expectancy of our S-Beam unit.
- The pneumatic cylinder delivers the compressive force of 113 lb. at 196,120 times a day.
- It is important to note that this particular load cell has a capacity of 100 lb.; therefore, we have been overloading this sensor for almost 15 years to demonstrate the high performance and quality of our product.
|
Arbor Press Verification
How it Works
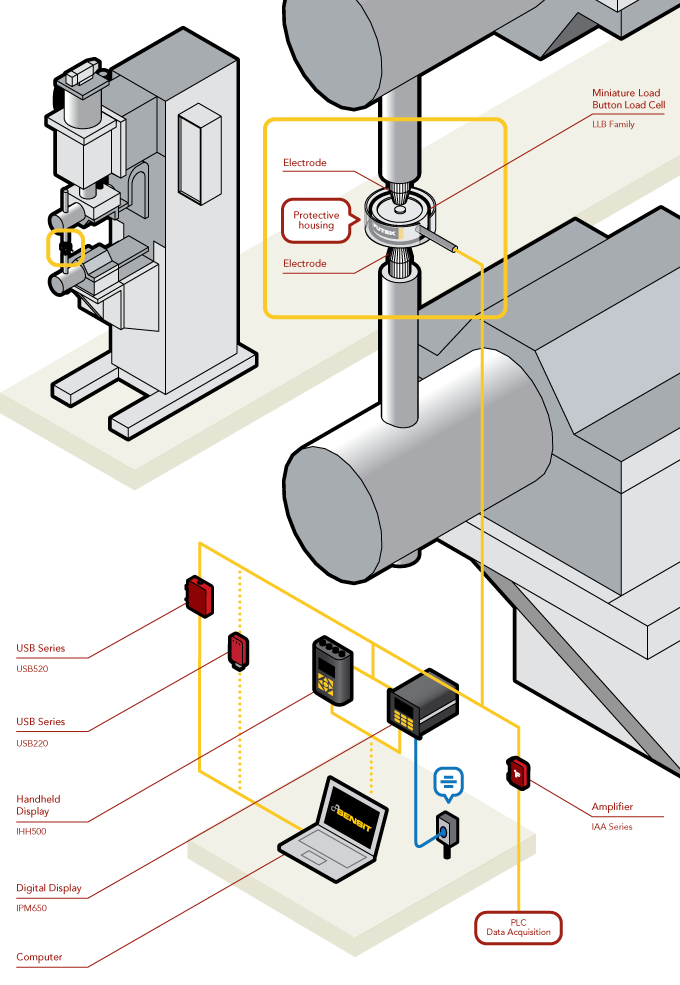
- Arbor presses are used to perform press fit and riveting processes. Quality Assurance Engineers utilize load cells to verify that the forces applied meet the process' specifications.
- In the above diagram, FUTEK's LLB Series Load Button has been positioned underneath the arbor press ram.
- As the engineer operates the press, measurement feedback can be displayed on either the IHH500 or IPM650, or streamed through USB directly onto a PC.
- This data can then be examined by the Q.A. department to confirm whether or not the operation meets the specifications.
|
Robotic Catheter Force Measurement
How it Works
- Catheter procedures demand the utmost precision and leave little margin for error.
- Feedback provided by the LSB200 gives physicians the necessary force measurements to navigate the catheter safely.
- In the above application, a Jr. Miniature S-Beam Load Cell (LSB200) is located on the guide wire extending from the robotic arm. The LSB200 measures tension on the wire and this information is used to control the direction and motion of the catheter.
- Measurement feedback can be streamed through FUTEK’s USB Solutions to a central control system.
|
Laparoscopic Tool Calibration
How it Works
- Load cells enable medical professionals to verify that clamping tools apply the appropriate amount of force before they are used in surgery.
- In this application, FUTEK’s Miniature Load Button (LLB130) is mounted to the grasping tip of a laparoscopic hand instrument. The load cell records force measurements, which can be used to calibrate the tool.
- Load feedback can be displayed on either FUTEK’s IHH500 or IPM650 digital displays, or streamed through USB to a PC. This data can then be examined to determine if the tool is suitable for operation or if it needs to be adjusted.
- Pairing the SENSIT™ Test and Measurement Software with any of FUTEK’s instruments provides the user with the ability to data log the measurements and store them for record keeping or calibration history.
|
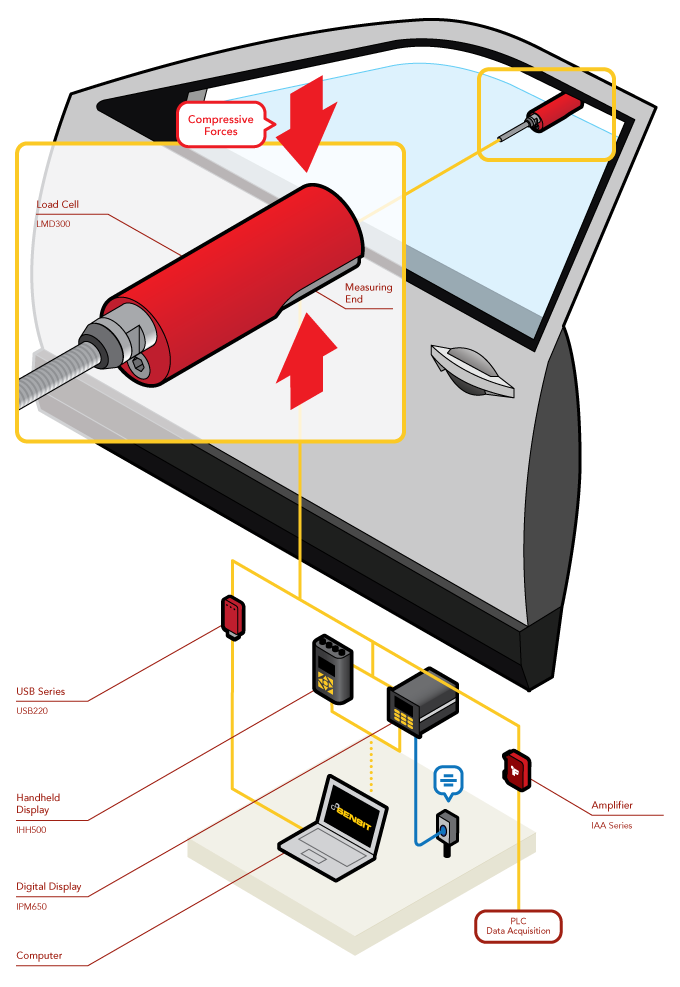
Power Window Pinch Test
How it Works
- Automakers use pinch force sensors to measure and record the closing force of a power window or sunroof.
- The LMD300 is a hand held unit placed between a power window and door frame. The load cell is then pinched and quantifies precise closing force measurement.
- These force measures can be streamed to a PC utilizing FUTEK's USB Solutions.
- Once streamed to a PC, that data can then be monitored by FUTEK's SENSIT™ Test and Measurement Software. SENSIT™ can monitor up to 16 channels of measurement readings, as well as live graph and data log.
|
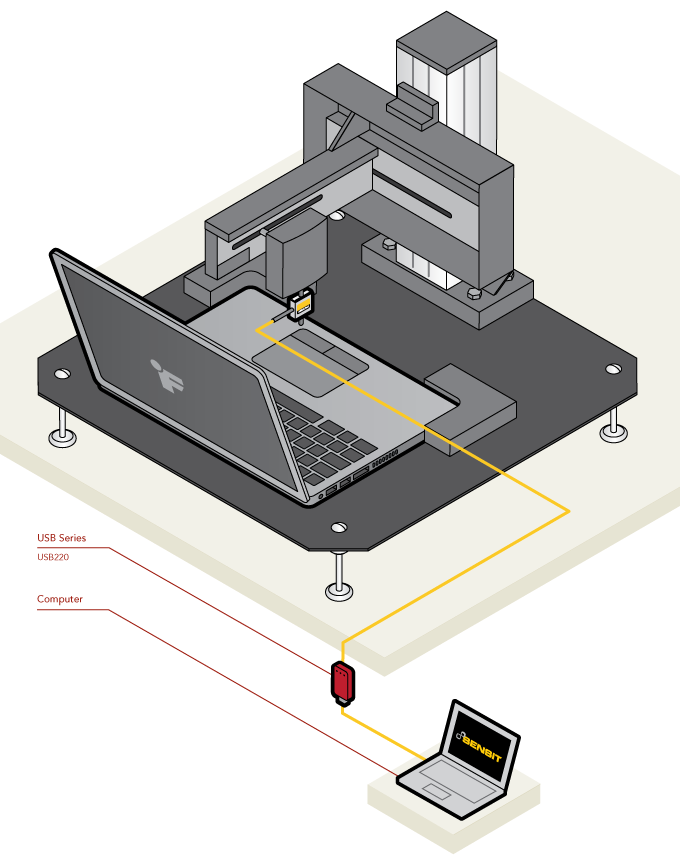
Trackpad / Touchpad Test Stand
How it Works
- Trackpads / Touchpads are a common feature of desktop computers and laptops.
- FUTEK’s LSB200 is fixed onto a testing actuator to quantify the force required to stimulate touchpad / trackpad response.
- During R&D, a test stand can be set up to record the force of pressing and dragging motion of a finger in relation of the position on trackpad.
- During quality checking processes, the gantry setup can be automated to inspect each trackpad to make sure the tactile feedbacks of a trackpad are within tolerance.
- These force measures can be streamed to a computer for control and analysis utilizing FUTEK's USB Solutions.
|
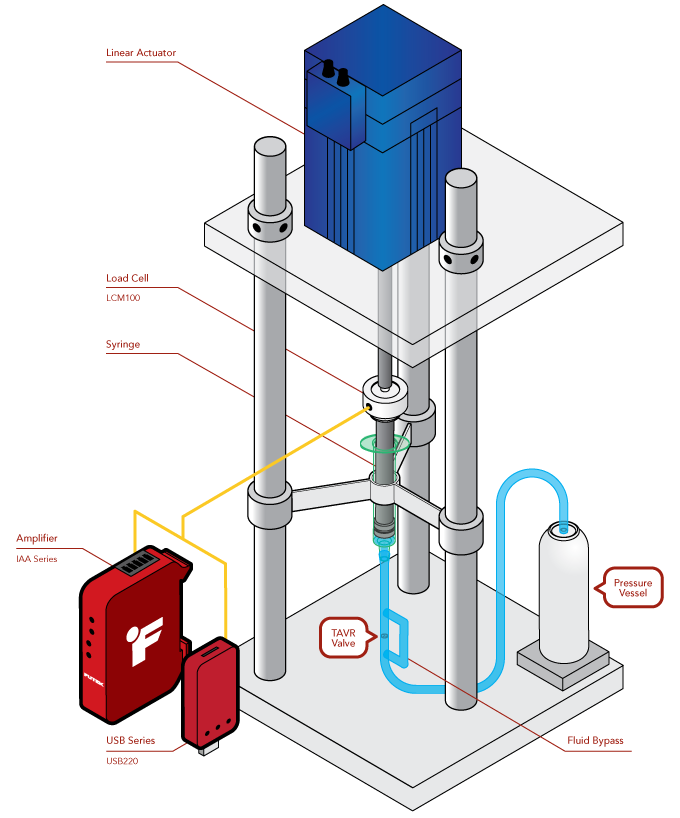
TAVR Valve Durability Testing
How it Works
- LCM series or LSB series load cells are threaded in-line with a linear actuator and syringe piston measuring the force the linear actuator is applying to the syringe piston for test validation.
- As the linear actuator pushes down on the load cell/piston assembly the flow of fluid pushes open the TAVR valve.
- A check valve keeps the fluid moving only through the TAVR valve and a pressure vessel is used as a reservoir allowing the system to reach the burst testing pressures.
- The linear actuator then retracts, pulling the piston up, forcing the TAVR closed and refilling through the now open check valve.
- The USB220 displays and logs the data to a PC via FUTEK's SENSIT™ software. This data can be used to validate the accuracy and precision of the pressure generated by the syringe piston.
|
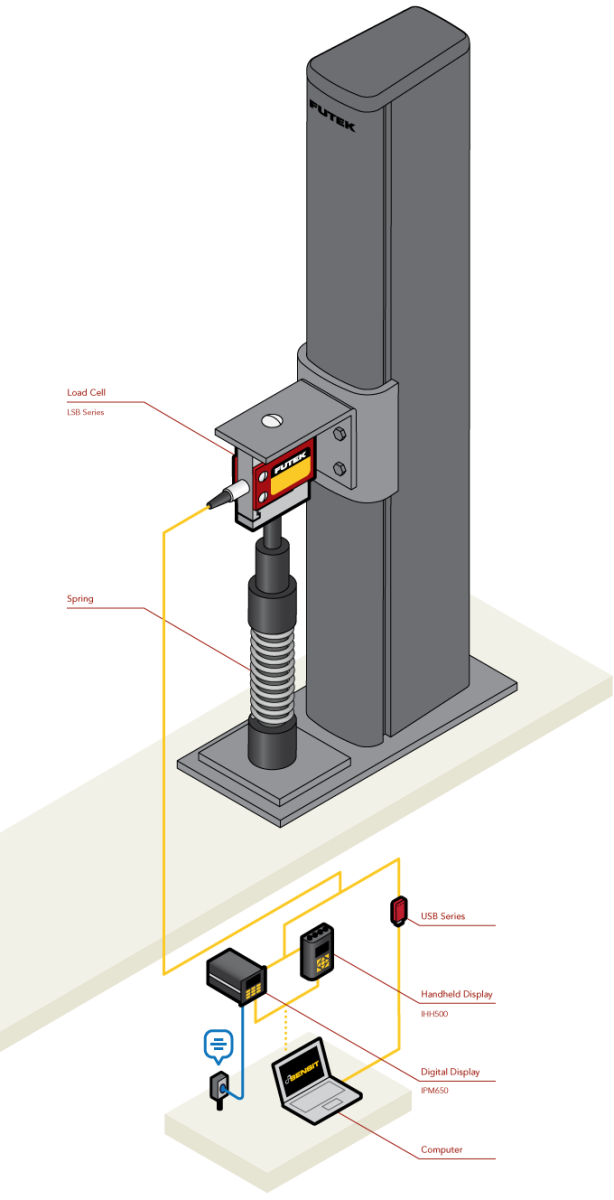
Spring Testing System
How it Works
- During R&D, the automated spring testing system can be configured to either compress or extend the spring under test.
- FUTEK’s LSB Series load cell is fixed onto the spring test column to measure spring compressive or tensile force when spring is compressed or elongated.
- These force measures can be streamed to a computer for analysis utilizing FUTEK’s USB Solutions.
- Information can then be used to determine or verify stiffness of spring via Hooke’s Law.
|
Wire Bond Testing
How it Works
- Wire bond testing systems enables two types of wire pull testing: destructive and non-destructive.
- During a destructive wire pull test, a wire is pulled upward (perpendicular to the substrate) by a hook until there is either a bond failure or the wire breaks. This type of test is intended for process setup.
- During a non-destructive wire pull test, a wire is pulled upward (perpendicular to the substrate) by a hook at a predesignated force to ensure high reliability packaging.
- Wire bond testing systems also have the ability to perform the following test: Solder Ball Shear, Die Shear, Stud Bump Pull, Passivation Layer Shear, Ribbon Pull, Tweezer Peel, Fatigue and Push.
- Specifically during a wire pull test FUTEK’s LSM300 precision load cell or LSB200 miniature load cell can be attached to the hook tool to measure the pulling force exerted on the wire under test.
- These force measures can be streamed to a computer for analysis utilizing FUTEK’s USB Solutions.
|