|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
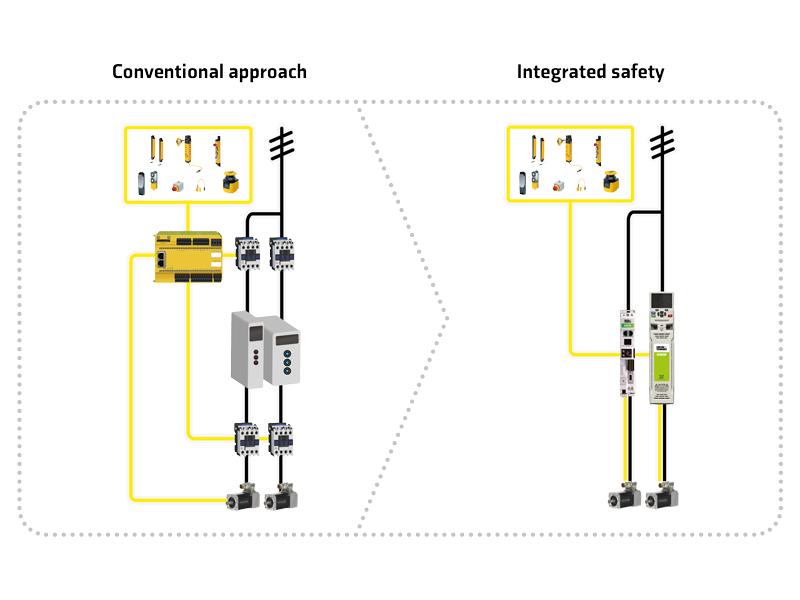
Functional SafetySafer machines with integrated safety
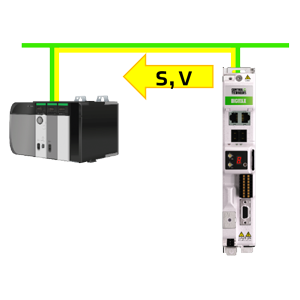
What is functional safety?Functional Safety entails the detection of a potentially dangerous condition resulting in the activation of a protective or corrective device or mechanism to prevent hazardous events arising or providing mitigation to reduce the consequence of the hazardous event. In the design of a machine, a risk assessment must be performed and then updated regularly. As far as possible, the machine should be designed to be inherently safe, so that hazards are eliminated from the basic design. However, in most cases some risks remain at an unacceptable level and must be actively reduced using suitable control measures. Why integrated safety?The integration of motion safety functions in the drive supports a decentralized approach to the machine's functional safety that brings many benefits
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reduce downtime with motion safetyWhen human intervention is required to carry out inspection and repair or simply during production, it is essential to protect personnel from interaction with dangerous moving parts. A comprehensive selection of Motion Safety Functions offers the flexibility to provide maximum protection whilst minimizing the impact on machine availability.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||






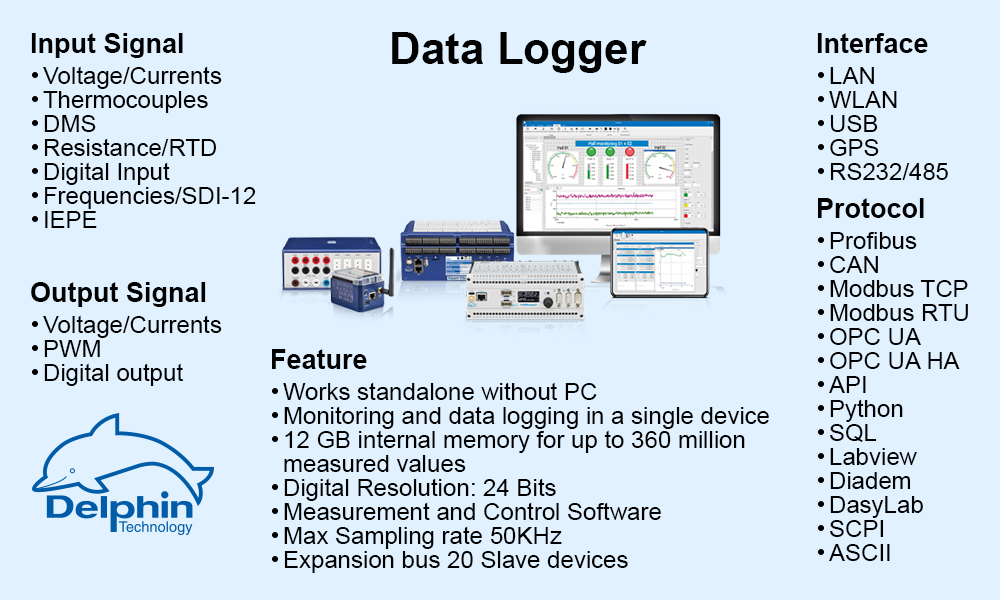
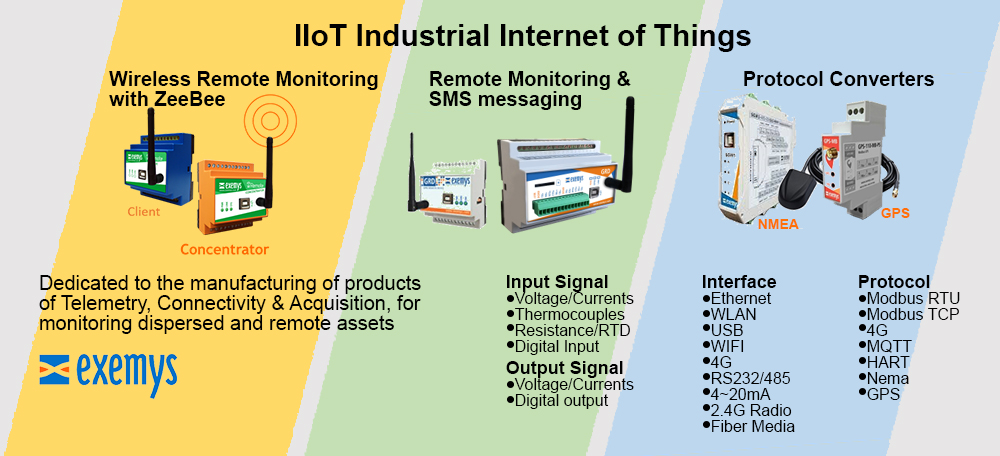












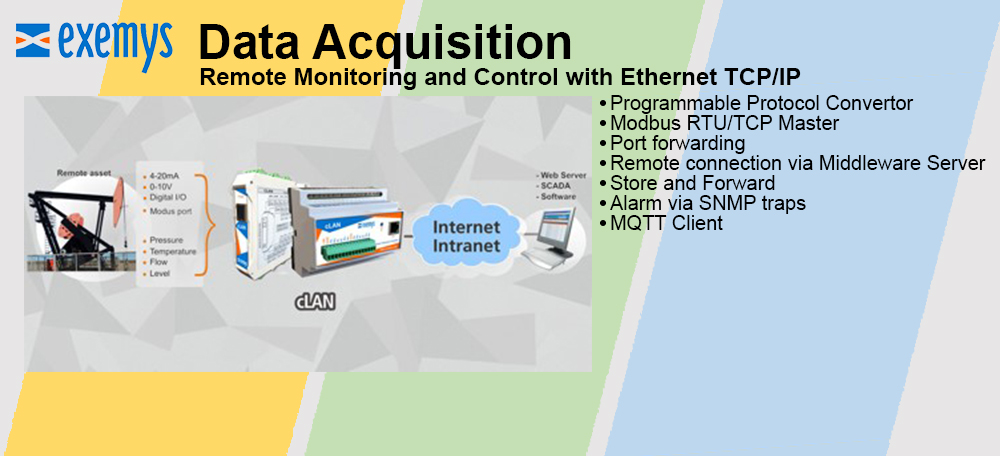
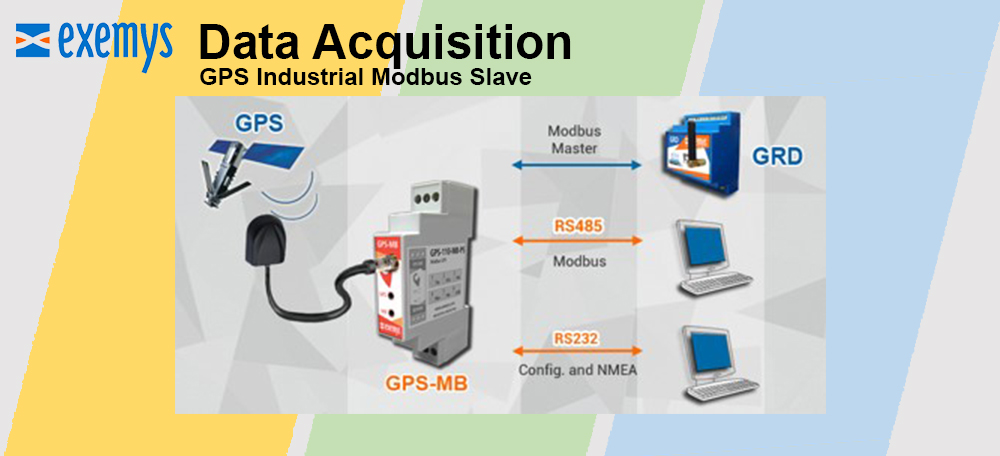
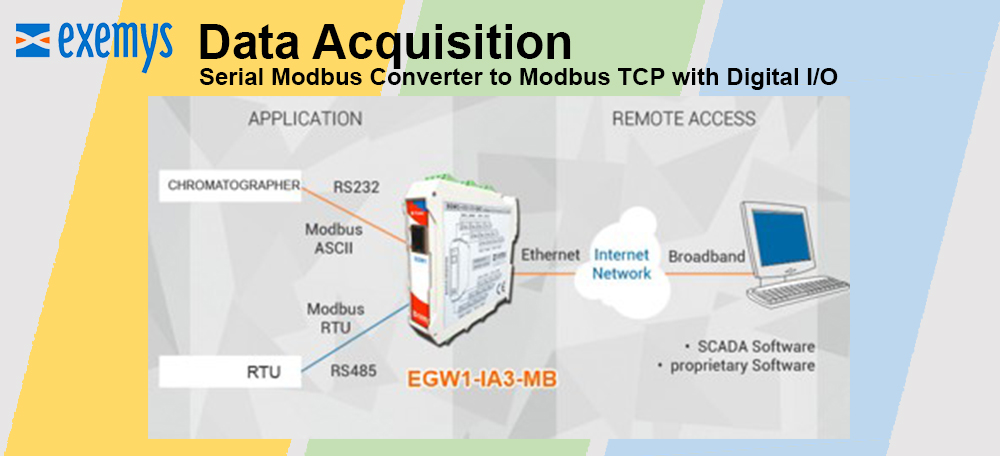

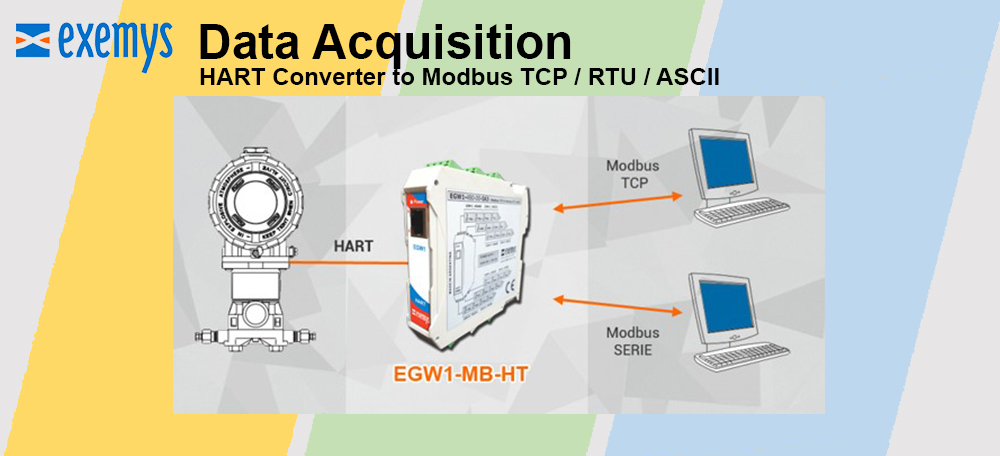
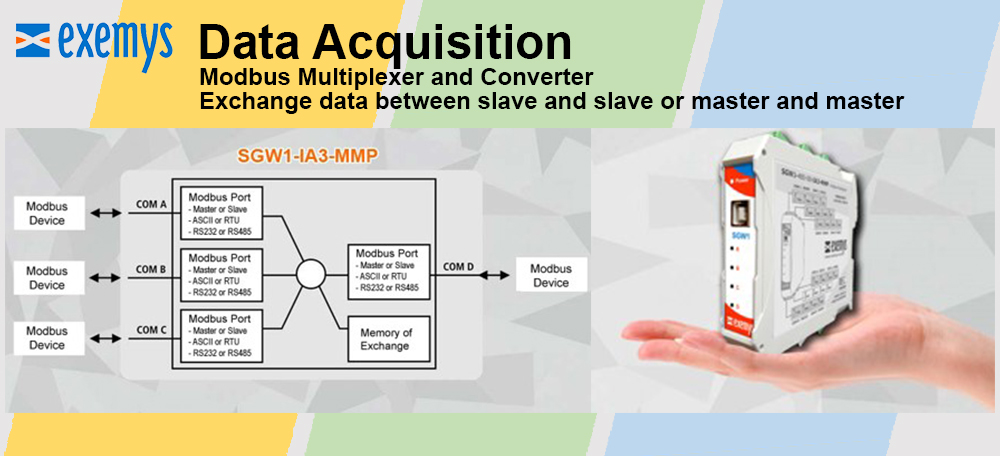
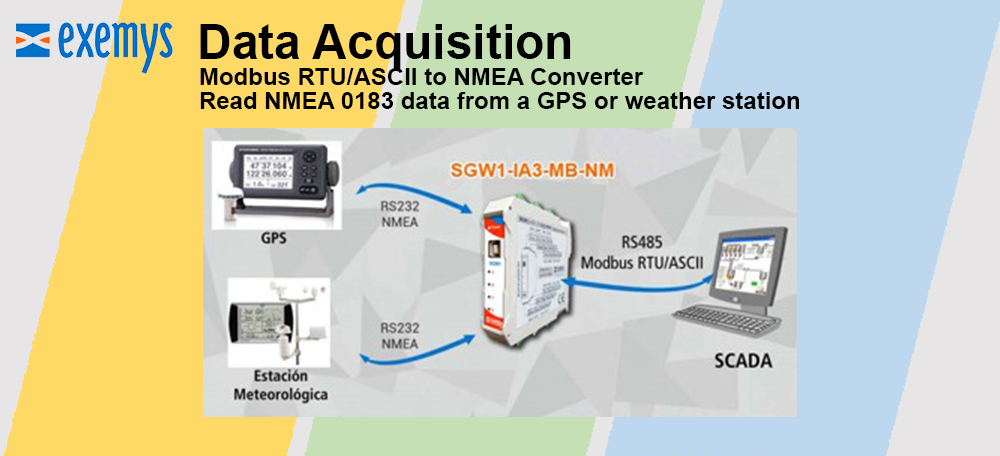

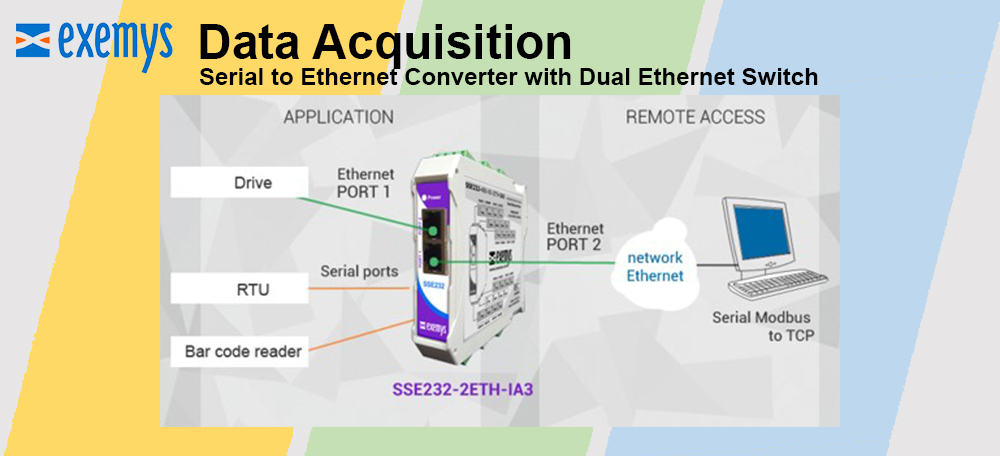
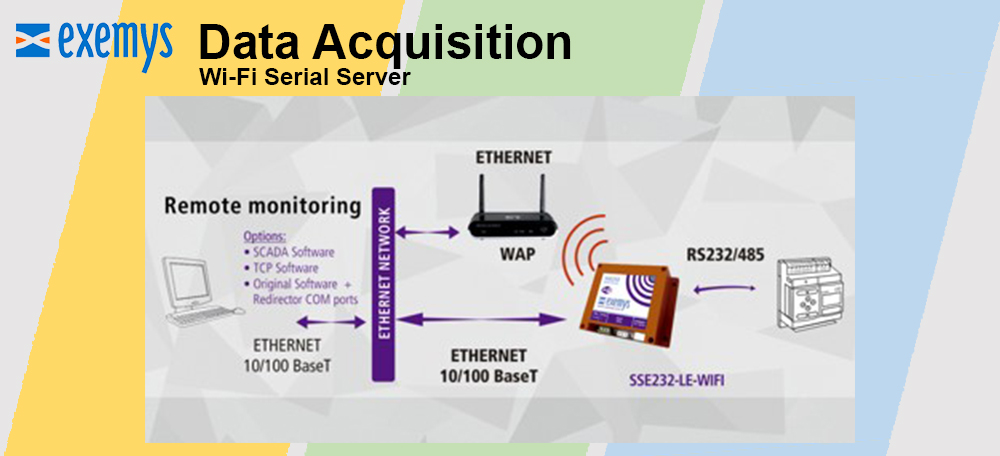









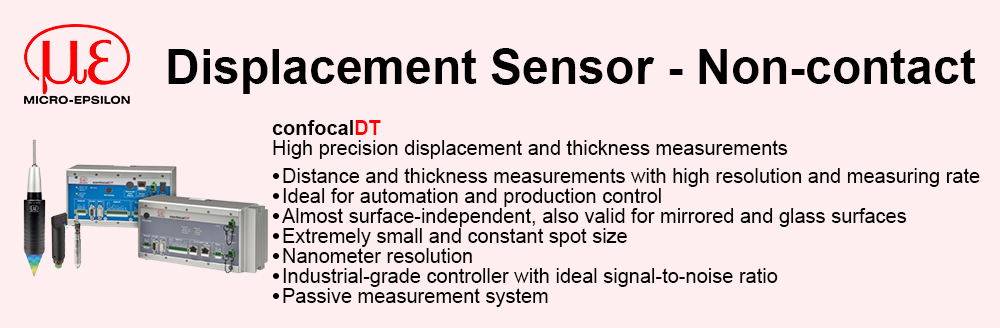
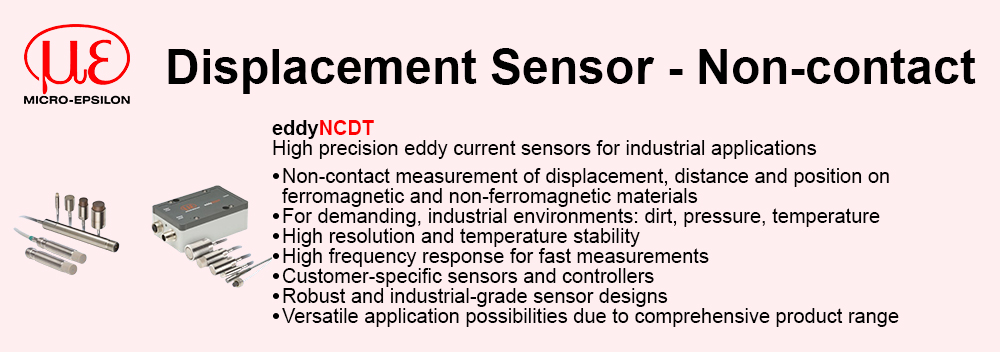
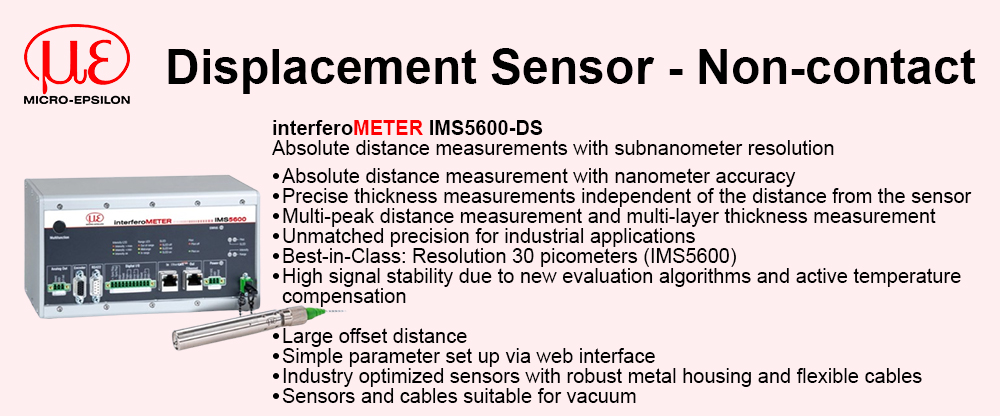
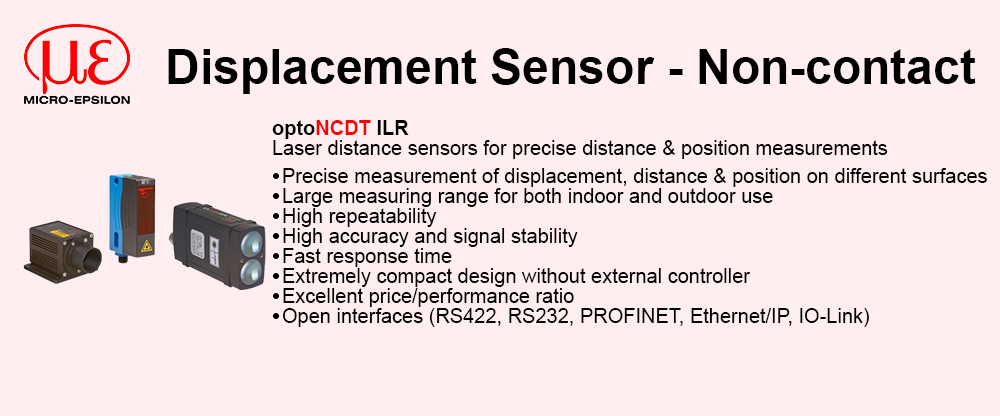
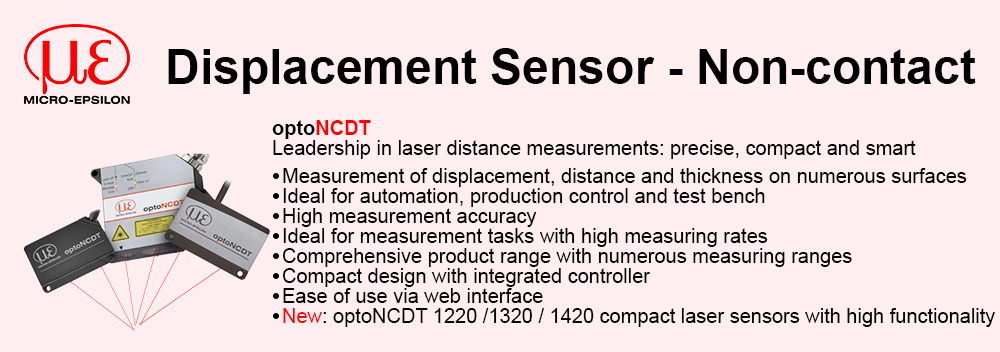
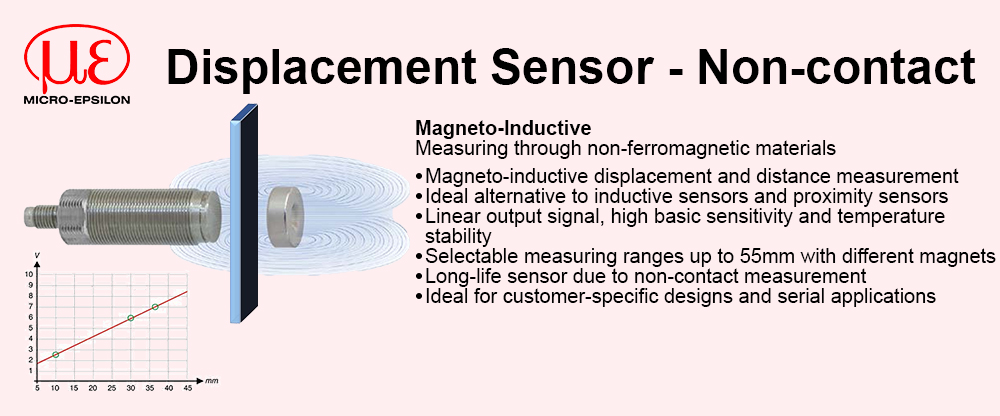
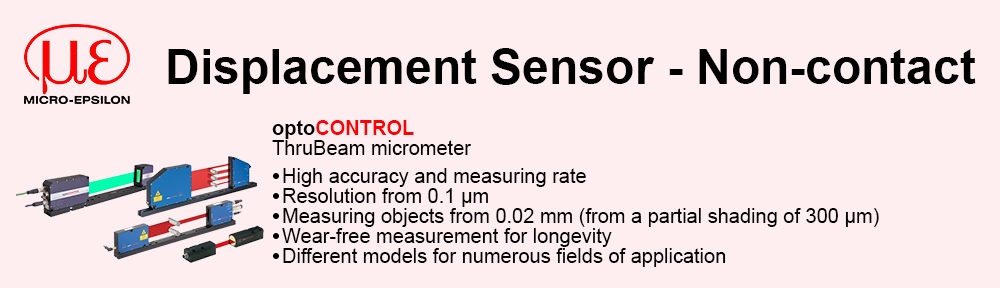
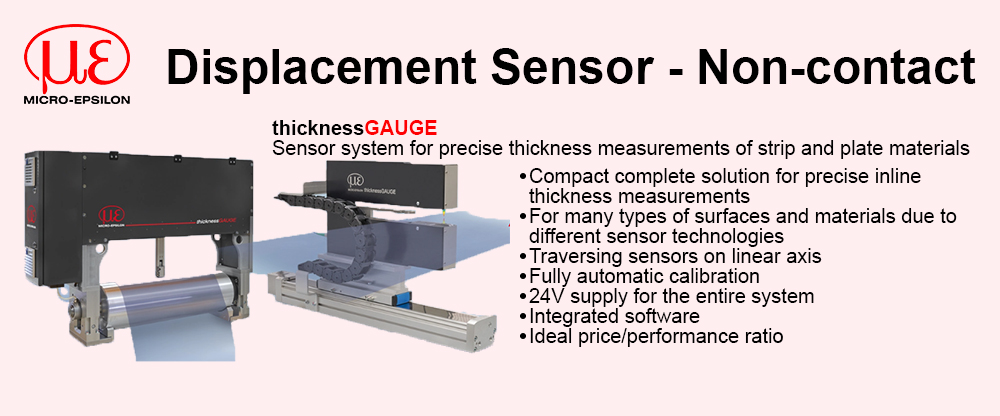









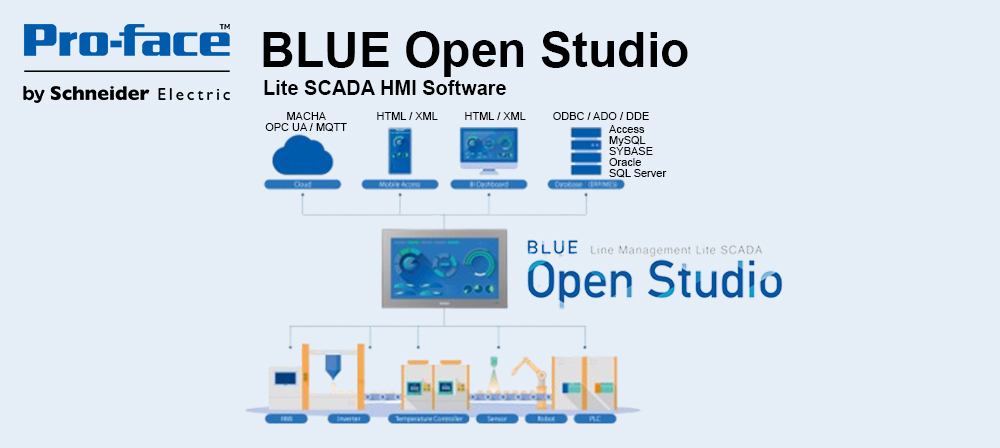










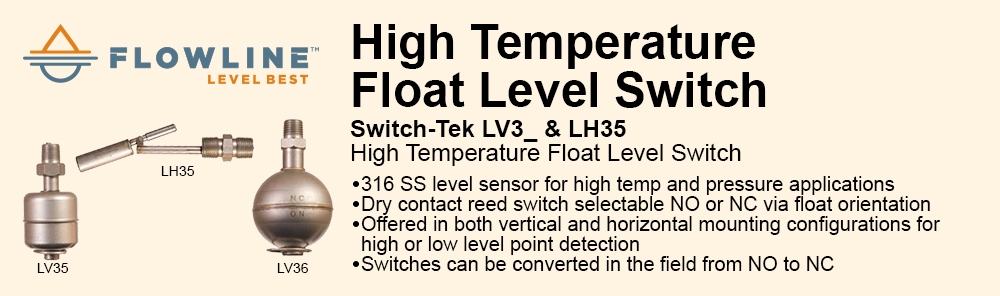







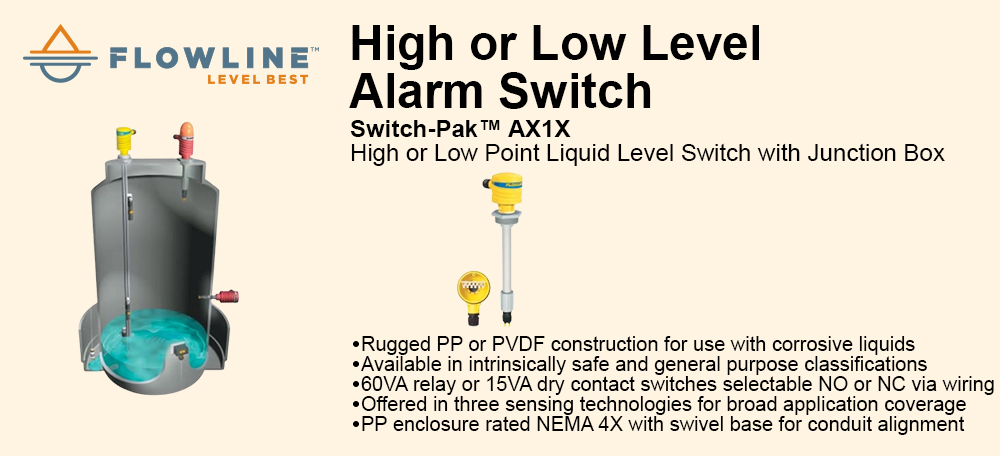

















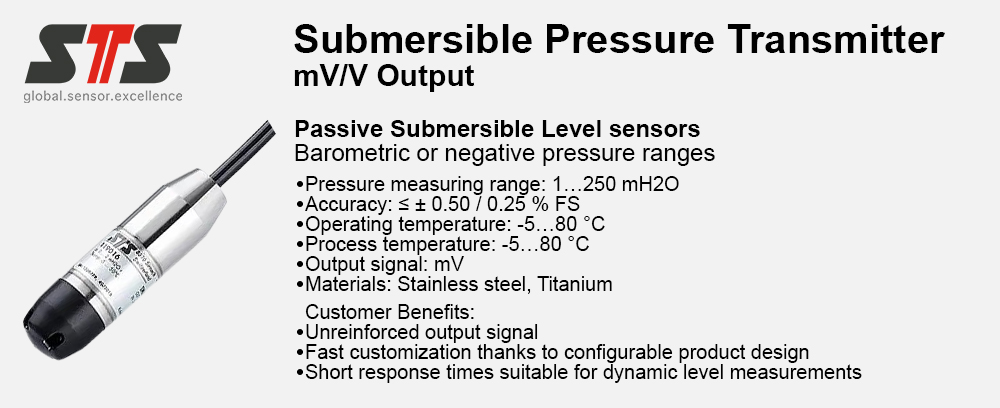
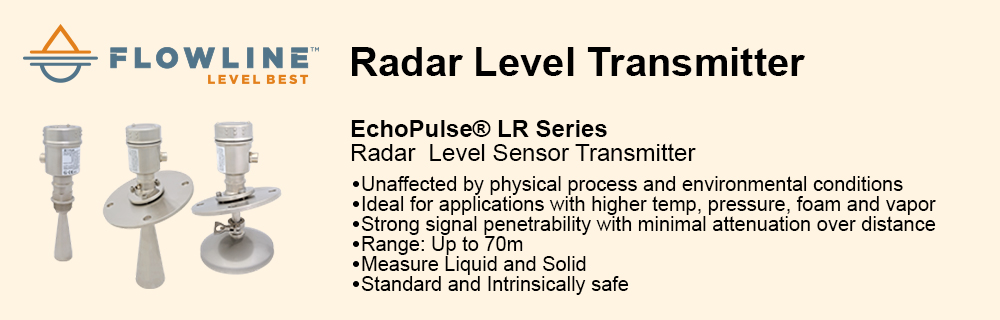






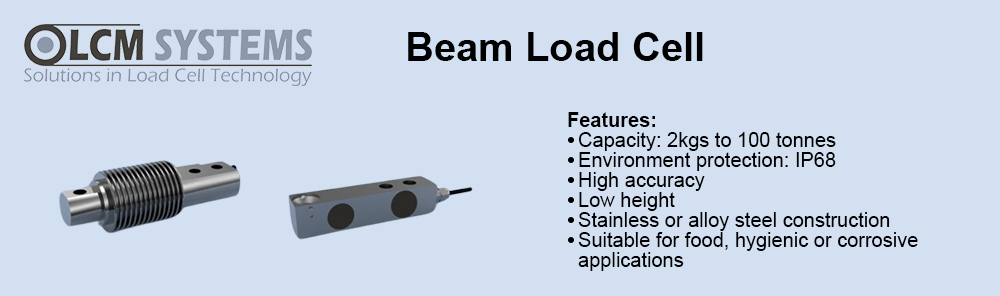
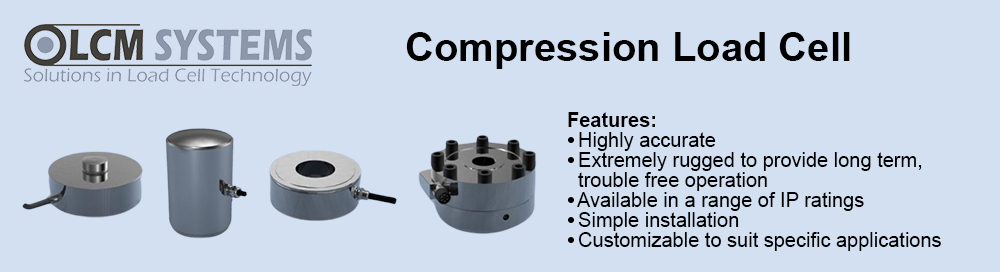






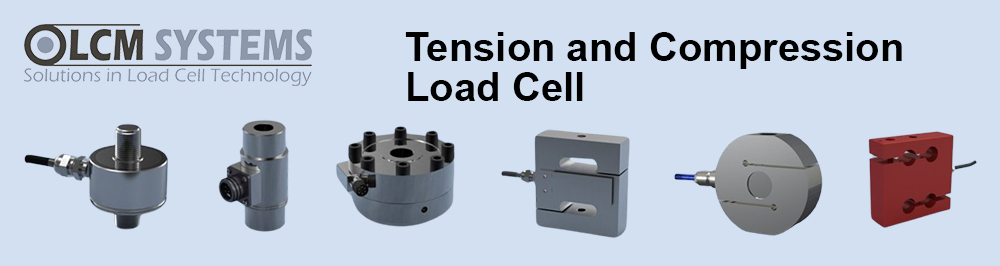





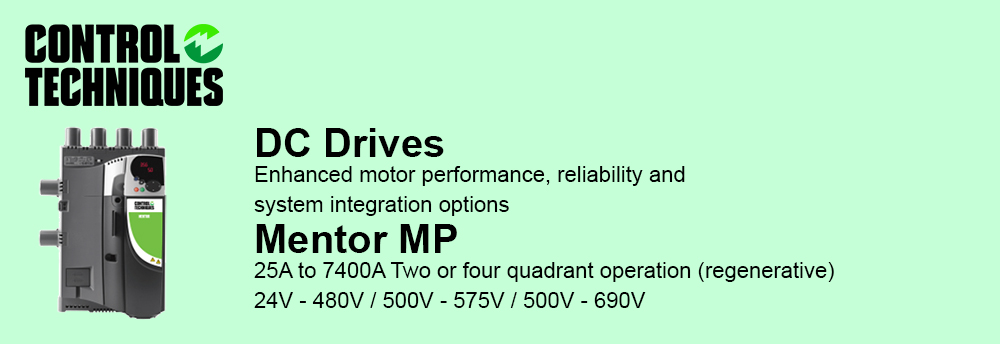

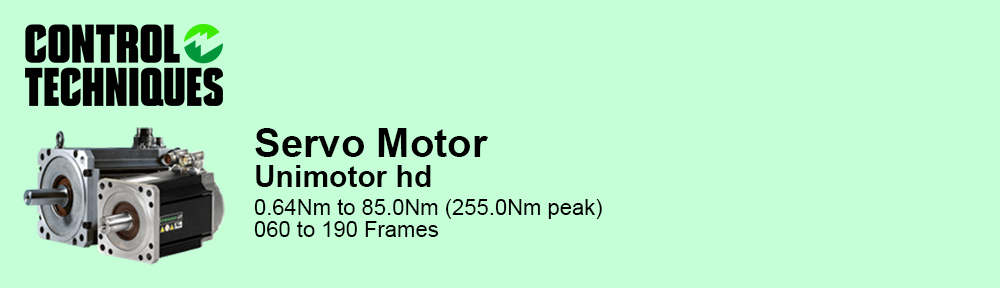

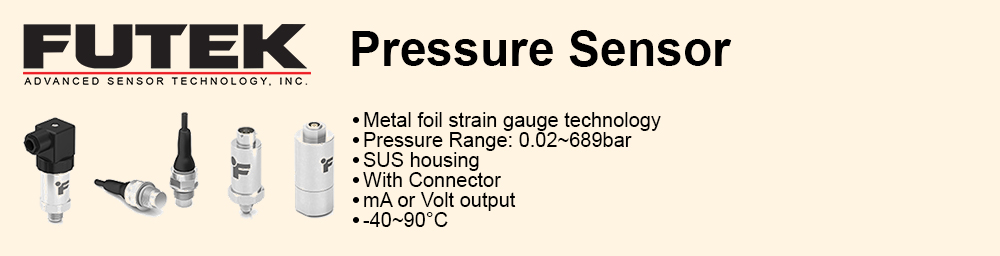


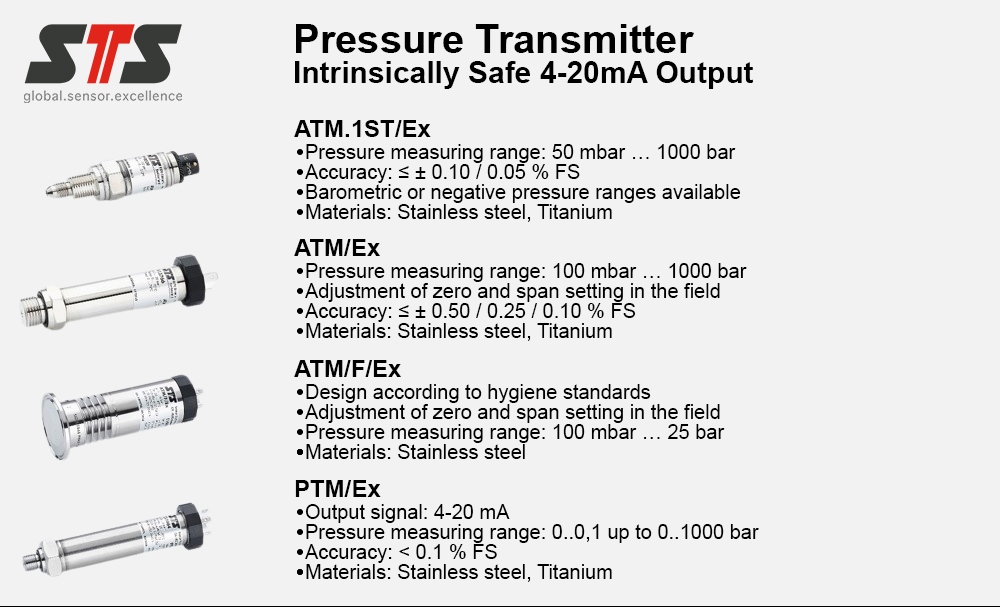




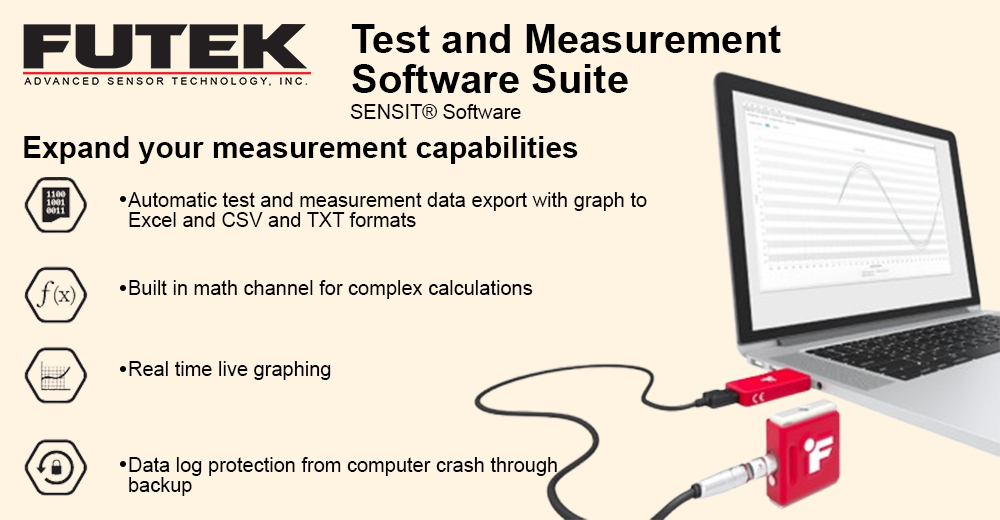

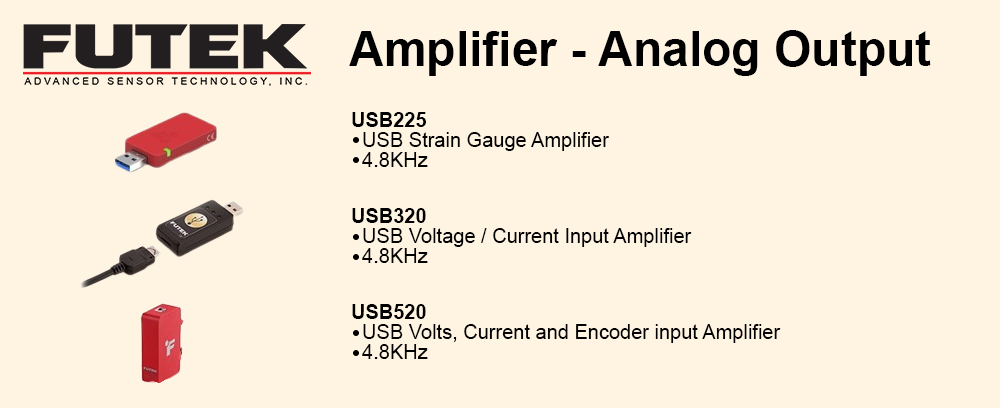
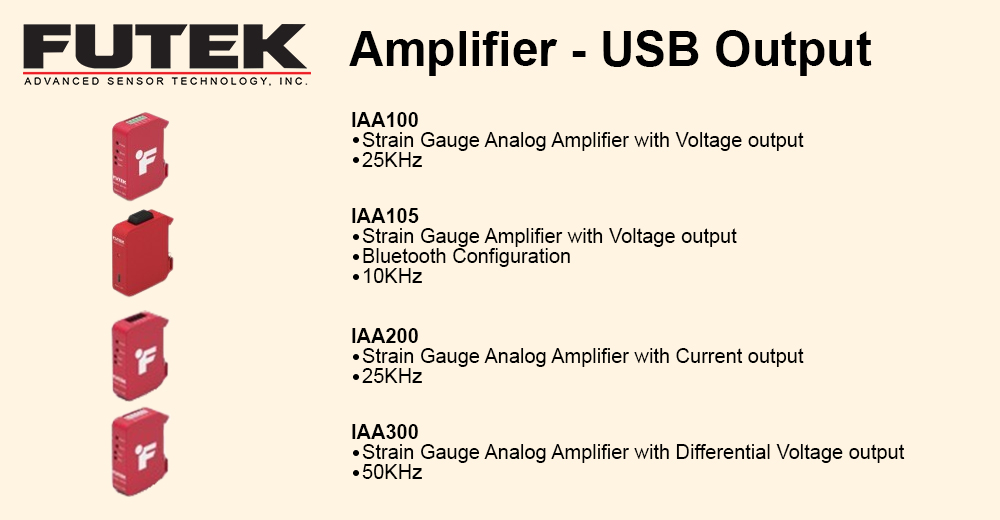
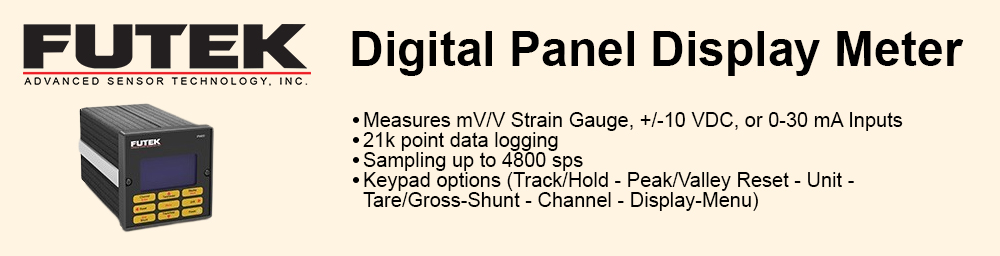













 Reduced complexity and therefore design time
Reduced complexity and therefore design time